The ultra-high volumetric energy density lithium-sulfur battery
Lithium ion battery technology (LIBs) is one of the most important mobile power sources for laptops, cameras, and smart phones. However, the current energy density of LIBs is approaching the theoretical limit, which underscoring the urgent need for new high energy density battery systems. Among the high-energy density storage systems, lithium-sulfur batteries, with energy density of 2600 Wh kg-1 (nearly 3~5 times than that of the traditional LIBs), holds the potential to serve as next generation of high energy battery. Sulfur possesses a very low electric conductivity of 5x10-30 S cm-1 at room temperature. Therefore, 30-70 wt. percent conductive materials, e.g. carbon nanotubes, graphene, porous carbon, and conductive polymers, have to be added into the electrode for high utilization of sulfur at current processing technology. The addition of nanocarbon materials with low stacking density neutralizes the high energy density, especially the volumetric energy density of lithium-sulfur batteries.
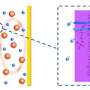
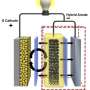
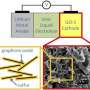
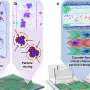
Researchers in Prof. Qiang Zhang's group from Tsinghua University in Beijing have developed a new strategy to increase the sulfur loading amount up to 90 wt percent in cathode materials based on an aligned CNT/S scaffold, which benefits the ultra-high volumetric energy density of lithium-sulfur batteries. A volumetric capacity of 1116 mAh・cm-3 and volumetric energy density of 434 Wh・L-1 were achieved based on the volume of the total cell, including cathode, current collector, membrane, anode, which was far beyond the lithium thin-film battery. The team has published their findings in a recent issue of Nano Energy (2014, 4, 65-72).
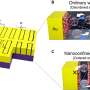
"The design of sulfur cathode materials for lithium sulfur batteries with high volumetric energy density is crucial for practical applications," said Qiang. "We selected aligned CNTs as the ultra-light scaffold because they demonstrate hierarchical porous architecture, extremely high electrical conductivity, low density, as well as low cost." In fact, such kinds of aligned CNTs with a length of 20-200 μm have been mass produced in a fluidized bed reactor at a low cost of less than $100 per kg-1. "These aligned CNTs can be easily dispersed into polymer with an ultra-low conductive percolation threshold of 0.0025 wt percent. Obviously, they can also serve as a high-efficiency conducting scaffold for sulfur materials." Prof. Fei Wei adds, "We have found a scalable, room-temperature, one-step method for the fabrication of an aligned CNT/sulfur cathode. The composite cathode material possesses ultra-high sulfur content of 90 wt percent and a high density of 1.98 g cm-3, which is 2 to 4 times than that of the routine sulfur/carbon composite cathode. Therefore, the volumetric energy density of this research is far beyond the reported result."
As Prof. Zhang points out, this approach sheds some light on building lithium-sulfur batteries with high volumetric energy density by using a high-density composite cathode with high sulfur loading amount. Future work in the development of lithium sulfur batteries may focus on the strategy of relieving the shuttle effect and suppressing the lithium dendrites, and further improvement in gravimetric and volumetric energy density of lithium-sulfur electrochemical systems.
More information: Xin-Bing Cheng, Jia-Qi Huang, Qiang Zhang, Hong-Jie Peng, Meng-Qiang Zhao, Fei Wei, Aligned carbon nanotube/sulfur composite cathodes with high sulfur content for lithium–sulfur batteries, Nano Energy, Volume 4, March 2014, Pages 65-72, ISSN 2211-2855, dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2013.12.013.
Provided by Tsinghua University