Cassini to probe Rhea for clues to Saturn rings

(PhysOrg.com) -- Saturn's icy moon Rhea might seem a strange place to look for clues to understanding the vast majestic rings encircling Saturn. But that's what NASA's Cassini spacecraft plans to do on its next flyby of Rhea. At closest approach, Cassini will pass within about 69 kilometers (43 miles) of the surface at 4:53 AM UTC on Tuesday, Jan. 11, which is 10:53 PM Pacific Time on Monday, Jan. 10. This flyby is the closest Cassini will get to the icy moon's surface.
Rhea, Saturn's second largest moon, is the best available chance for studying how often tiny meteoroids bombard a surface. Rhea has almost no atmosphere, which allows Cassini's cosmic dust analyzer and radio and plasma wave instrument to detect the dusty debris that flies off the surface from tiny meteoroid bombardments. Counting these dust particles ejected from Rhea's surface helps scientists estimate the bombardment rate for the Saturn system and how often the icy rings have been polluted by particles from other places in the solar system. Understanding the contamination rate will enable scientists to improve estimates of the age of the rings.
Previous attempts to count this rate in the inner part of the Saturn system have been confounded by the dusty E ring, made of icy particles spewed by the moon Enceladus. But at Rhea, scientists can sufficiently filter out the E-ring effect. The cosmic dust analyzer will also be set to look for smaller particles than it looked for during a previous Rhea flyby in March 2010.
The upcoming flyby will also enable scientists to gather more data on Rhea’s very thin oxygen-and-carbon-dioxide atmosphere that was recently discovered by Cassini scientists using the ion and neutral mass spectrometer and the Cassini plasma spectrometer. Fields and particles instruments will also investigate the interaction between Rhea and the magnetic bubble around Saturn known as the magnetosphere.
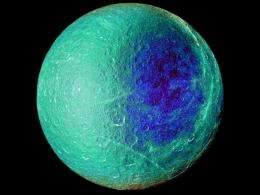
Cassini will also snap pictures of the Rhea surface, a venture that will include making a global mosaic of such regions as the large Tirawa basin and the dark bluish spots around Rhea's equator. The imaging cameras will also take another look to see if there is any more evidence of a ring around Rhea.
This is the third close flyby of Saturn's moon Rhea. The closest flyby before this one was 100 kilometers (60 miles) in altitude.
Provided by JPL/NASA


















