Earth Sciences
New 3D models reveal how warming climate affects underwater ocean tides
Few things in nature are as predictable as ocean tides. Driven by the moon's and sun's gravitational pull, these persistent, short-period, and large-magnitude phenomena are apparent in nearly all types of oceanographic and ...
1 hour ago
0
1

Legacy of Indigenous stewardship of camas dates back more than 3,500 years, study finds
An Oregon State University study has found evidence that Indigenous groups in the Pacific Northwest were intentionally harvesting edible camas bulbs at optimal stages of the plant's ...
An Oregon State University study has found evidence that Indigenous groups in the Pacific Northwest were intentionally harvesting edible camas bulbs at ...
Archaeology
1 hour ago
0
0
A model outlining the microscopic origin of black hole entropy
Black holes are intriguing astronomical objects that have a gravitational pull so strong that it prevents any object and even light from escaping. While black holes have been the topic ...
Black holes are intriguing astronomical objects that have a gravitational pull so strong that it prevents any object and even light from escaping. While ...

Alaska's rusting waters: Pristine rivers and streams turning orange
Dozens of Alaska's most remote streams and rivers are turning from a crystal clear blue into a cloudy orange, and the staining could be the result of minerals exposed by thawing permafrost, ...
Dozens of Alaska's most remote streams and rivers are turning from a crystal clear blue into a cloudy orange, and the staining could be the result of ...
Earth Sciences
2 hours ago
0
1

New quantum dot approach can enhance electrical conductivity of solar cells
A team led by Professor Jongmin Choi of the Department of Energy Science and Engineering has developed a PbS quantum dot that can rapidly enhance the electrical conductivity of solar cells. The findings are published in the ...
Nanomaterials
2 hours ago
0
25

Biologists travel with their mobile laboratory to study a wide range of mitochondrial functions in avian migration
For Wendy Hood and Geoffrey Hill in Biological Sciences, Andreas Kavazis in Kinesiology, and their team, Emma Rhodes, Paulo Mesquita, and Jeff Yap, traveling the country to unlock the mystery of mitochondria in migrating ...
Plants & Animals
1 hour ago
0
0

Can coal mines be tapped for rare earth elements?
Deposits of designated critical minerals needed to transition the world's energy systems away from fossil fuels may, ironically enough, be co-located with coal deposits that have been mined to produce the fossil fuel most ...
Earth Sciences
2 hours ago
0
13

Genetic drift, not natural selection, identified as main factor driving speciation in endangered pupfish species
Scientists have identified a new member on the genetic family tree of an endangered pupfish native to south-central New Mexico.
Plants & Animals
2 hours ago
0
1

How cockroaches spread around the globe to become the pest we know today
They're six-legged, hairy home invaders that just won't die, no matter how hard you try.
Plants & Animals
2 hours ago
0
0

Underwater signals generated by open sea airplane crashes could be key to detecting final resting place of MH370
Signals captured on underwater microphones could be key to locating airplanes such as MH370 when they crash into the ocean, Cardiff University research shows.
Engineering
1 hour ago
1
0

New robotic palm uses sophisticated tactile sensors to mimic human touch
"I'll have you eating out of the palm of my hand" is an unlikely utterance you'll hear from a robot. Why? Most of them don't have palms.
Robotics
1 hour ago
0
0

AI trained to draw inspiration from images, not copy them
Powerful new artificial intelligence models sometimes, quite famously, get things wrong—whether hallucinating false information or memorizing others' work and offering it up as their own. To address the latter, researchers ...
Machine learning & AI
2 hours ago
0
0

The Future is Interdisciplinary
Find out how ACS can accelerate your research to keep up with the discoveries that are pushing us into science’s next frontier
 Medical Xpress
Medical Xpress

Why nightmares and 'daymares' could be early warning signs of autoimmune disease

Study sheds light on bacteria associated with pre-term birth

New device helps paraplegics regain partial use of hands

Researchers find intriguing connections between Alzheimer's disease and other common conditions
New AI algorithm may improve autoimmune disease prediction and therapies

Researchers uncover biological trigger of early puberty
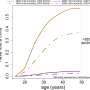
Researcher finds mothers live longer as child mortality declines
Women face worse chronic kidney disease management in primary care

Improving online depression treatment

New mechanisms underlying tumor variety in brain cancers discovered
 Tech Xplore
Tech Xplore

AI trained to draw inspiration from images, not copy them

Microsoft unveils 'AI-ready' PCs
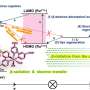
Researchers successfully develop next-gen semi-permanent battery technology
AI chips could get a sense of time with memristor that can be tuned

Microsoft's AI chatbot will 'recall' everything you do on a PC

South Korea, Britain host AI summit with safety top of agenda

ChatGPT is now better than ever at faking human emotion and behavior

After hundreds of years, study confirms Bermuda now home to cownose rays
For hundreds of years, the whitespotted eagle ray (Aetobatus narinari) has been considered the only inshore stingray species in Bermuda, until now.
Plants & Animals
3 hours ago
1
1

Increasing drought puts the resilience of the Amazon rainforest to the test
Since 2015, the Amazon has been slower to recover from increasing drought events, but, overall, the rainforest still shows a remarkable resilience. New international research led by KU Leuven Earth and environmental scientists ...
Earth Sciences
1 hour ago
0
0

Researchers analyze how a chemical process could help recycle a common plastic waste
Researchers at Virginia Tech are exploring processes that might greatly increase the recycling of one of the world's most-produced plastics.
Polymers
3 hours ago
0
39

Study finds cloudy waters may drive African fish to develop bigger eyes
Variations in water quality can impact the development of the visual system of one species of African fish, suggests a new study.
Plants & Animals
3 hours ago
0
11

Satellite radar data uncover 'vigorous melting' at Antarctica's Thwaites Glacier
A team of glaciologists led by researchers at the University of California, Irvine used high-resolution satellite radar data to find evidence of the intrusion of warm, high-pressure seawater many kilometers beneath the grounded ...
Earth Sciences
3 hours ago
0
0

Lipid nanoparticle-mRNA regimen reverses inflammation and aids recovery from diabetic wounds in mice
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have designed a regenerative medicine therapy to speed up diabetic wound repair. Using tiny fat particles loaded with genetic instructions to calm down inflammation, ...
Bio & Medicine
3 hours ago
0
70

By listening, scientists learn how a protein folds
By converting their data into sounds, scientists discovered how hydrogen bonds contribute to the lightning-fast gyrations that transform a string of amino acids into a functional, folded protein.
Biochemistry
3 hours ago
0
0

Research shows linked biological pathways driving skin inflammation
A certain biological pathway—a set of linked reactions in the body—drives the inflammation seen in the skin disease psoriasis, a new study finds. The work could lead to improved therapies for all inflammatory skin diseases, ...
Immunology
3 hours ago
0
3

Electric school buses may yield significant health and climate benefits, cost savings
Replacing diesel school buses with electric school buses may yield up to $247,600 in climate and health benefits per individual bus, according to a new study by researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The ...
Energy & Green Tech
3 hours ago
2
1

Bioluminescence and 3D-printed implants shed light on brain–spinal interactions
A sensory process such as pain is no ordinary phenomenon—it's a symphony of neural and vascular interactions orchestrated by the brain and spinal cord. Attempting to dissect this symphony by focusing on a single region ...
Neuroscience
3 hours ago
0
15

Illegitimate interruptions reduce productivity in the workplace, finds study
A team of researchers from The University of Queensland has found employees experience more stress at work when interrupted with requests for unnecessary or unreasonable tasks.

NASA study provides new look at orbital debris, potential solutions
New data analysis indicates that NASA and its partners could have more cost-effective methods for dealing with the growing issue of orbital debris than previously thought.

Appropriate exercise is an important part of crew health during space missions
Future missions to the moon and Mars must address many challenges, including preventing loss of bone and muscle tissue in astronauts. Research on the International Space Station is helping to address this challenge.
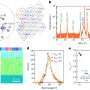
Researchers identify the principle behind 'soft mechanoluminescent complex'
A research team collaborated to identify the principle of an eco-friendly energy-based soft mechanoluminescent complex that emits light without batteries. It is expected to be applied in various fields, such as optical sensors, ...

From 'yellow peril' to COVID-19: New book takes unflinching look at anti-Asian racism
More than 150 years ago, some 15,000 Chinese workers arrived in the U.S. to help construct the country's first transcontinental railroad, which connected the West Coast with the East Coast's rail network.

Study shows alkyl-aromatic hybrid micelles can form from emergent umbrella-shaped molecules
Micelles assemble in water from amphiphilic molecules, composed of hydrophilic and hydrophobic frameworks. They can be found all around us, for example in soaps, detergents, and shampoos. Their main application is the water-solubilization ...

Decarbonization dynamics: New analysis unveils shifting trends in the voluntary carbon offset market
As humanity grapples with the fight against climate change, reducing greenhouse gas emissions is urgently necessary. One way to achieve this is through the carbon offset market, where organizations or individuals can buy ...

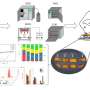
Researchers investigate mercury concentrations in fish and wildlife on a global scale
A paper, titled "Global Mercury Concentrations in Biota: Their Use as a Basis for a Global Biomonitoring Framework" and published in the journal Ecotoxicology, describes for the first time currently available mercury data ...
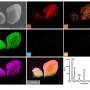
Comparison of four methods on drying efficiency and physicochemical properties of chicken meat
Chicken breast jerky (CBJ) is a popular pet food due to its high crude protein content and long shelf life. In the production of CBJ, the drying process is a crucial step. However, the physicochemical and functional properties ...

Combating air pollution in China: Why secondary pollutants are now a primary concern
Like most countries, China has had its problems with air pollution. However, over the last decade, a series of successful measures implemented by the Chinese government have resulted in an impressive improvement in air quality.

Melon flavor decoded: The genetic keys to aromatic diversity
Melon aroma greatly influences consumer preference and fruit quality. Climacteric melons produce more esters, while non-climacteric melons have more aldehydes. Understanding these genetic differences is crucial for breeding ...

The genetic interplay in Impatiens downy mildew: A transcriptome-based approach to enhancing disease resistance
A research team has meticulously analyzed the transcriptional response of Impatiens walleriana to Plasmopara obducens infection, revealing between 3,000 and 4,500 differentially expressed transcripts at various stages of ...
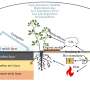
Plastic-greenhouse agriculture: A novel soil profile design for global sustainability and enhanced crop production
A research team has developed a novel conceptual framework for designing plastic-greenhouse soil profiles that cater to the needs of smallholder farmers. The soil profile includes four functional layers: a soil mulch layer ...
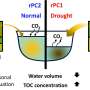
Unraveling the drought dilemma in South Korea: Can reservoirs be a carbon source?
Researchers analyzed water quantity and quality data from domestic agricultural reservoirs to shed light on the hydrological impacts of a severe drought on degrading the water quality.

Q&A: How tea may have saved lives in 18th century England
Drinking tea can have several health benefits. There is seemingly a brew for everything from sleep to inflammation to digestion. In 18th century England, however, drinking tea may have saved a person's life, and it likely ...

NASA, Sierra Space deliver Dream Chaser spaceplane to Florida for launch preparation
As part of NASA's efforts to expand commercial resupply in low Earth orbit, Sierra Space's uncrewed spaceplane arrived at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of its first flight to the International Space Station.
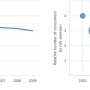
Evolving market dynamics foster consumer inattention that can lead to risky purchases, says researchers
Researchers have developed a new theory of how changing market conditions can lead large numbers of otherwise cautious consumers to buy risky products such as subprime mortgages, cryptocurrency or even cosmetic surgery procedures.

Researchers find that refrigerating or air-drying soil samples for future studies retains important microbial details
Post-doctoral researcher Joe Edwards and graduate student Sarah Love, both in the University of Tennessee at Knoxville's Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, have published published findings this spring that can ...

Expanding on the fundamental principles of liquid movement
From the rain drops rolling down your window, to the fluid running through a COVID rapid test, we cannot go a day without observing the world of fluid dynamics. Naturally, how liquids traverse across, and through, surfaces ...

Seeing the color of entangled photons in molecular systems
Spectroscopy is the study of how matter absorbs and emits light and other radiation. It allows scientists to study the structure of atoms and molecules, including the energy levels of their electrons. Classical optical spectroscopy ...