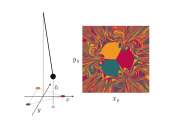
Testing a machine learning approach to geophysical inversion
A common problem in the geosciences is the need to deduce unseen physical structure based on limited observations. For instance, a ground-penetrating radar observation attempts to infer underground structure without any in ...