Laser imaging could offer early detection for at-risk artwork
Look closely at Impressionist paintings in museums compared with photos of them taken 50 years ago, and you might notice something odd: Some are losing their bright yellow hues.
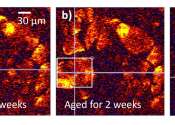
Look closely at Impressionist paintings in museums compared with photos of them taken 50 years ago, and you might notice something odd: Some are losing their bright yellow hues.
Optics & Photonics
Apr 29, 2024
0
36

A team led by atmospheric scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory has demonstrated the first-ever remote observations of the fine-scale structure at the base of clouds. The results, just ...
Earth Sciences
Apr 24, 2024
0
159

Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a recent study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval, the second, mitigating some of the ...
General Physics
Apr 22, 2024
0
107

EPFL researchers have developed the first comprehensive model of the quantum-mechanical effects behind photoluminescence in thin gold films; a discovery that could drive the development of solar fuels and batteries.
Nanophysics
Apr 19, 2024
0
86

In principle, one shouldn't compare apples to oranges. However, in topology, which is a branch of mathematics, one must do just that. Apples and oranges, it turns out, are said to be topologically the same since they both ...
Quantum Physics
Apr 18, 2024
0
160

Multi-photon 3D laser printing has revolutionized miniature fabrication, but limitations in speed and material compatibility have held it back. Now, researchers have taken a giant leap forward, achieving a tenfold increase ...
Optics & Photonics
Apr 8, 2024
0
25

Plants are made up of very rigid cells. Much like bricks in a wall, this feature gives them the structural support to maintain their shape and to stand upright against gravity. However, just like any living organism, plants ...
Plants & Animals
Apr 4, 2024
1
21

One of the most fundamental interactions in physics is that of electrons and light. In an experiment at Goethe University Frankfurt, scientists have now managed to observe what is known as the Kapitza-Dirac effect for the ...
Optics & Photonics
Apr 3, 2024
0
176

Focusing a tailored laser beam through transparent glass can create a tiny spot inside the material. Researchers at Tohoku University have reported on a way to use this small spot to improve laser material processing, boosting ...
Optics & Photonics
Mar 27, 2024
0
115
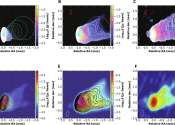
An international team led by Dr. Yuan Feng from Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has investigated the validity of the two main models of black hole jets by calculating the radiation predicted ...
Astronomy
Mar 25, 2024
0
38
A laser is a device that emits light (electromagnetic radiation) through a process called stimulated emission. The term laser is an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Laser light is usually spatially coherent, which means that the light either is emitted in a narrow, low-divergence beam, or can be converted into one with the help of optical components such as lenses. Typically, lasers are thought of as emitting light with a narrow wavelength spectrum ("monochromatic" light). This is not true of all lasers, however: some emit light with a broad spectrum, while others emit light at multiple distinct wavelengths simultaneously. The coherence of typical laser emission is distinctive. Most other light sources emit incoherent light, which has a phase that varies randomly with time and position.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA