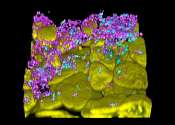
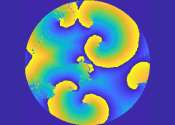
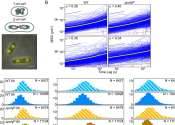
Study suggests host response needs to be studied along with other bacteriophage research
A team of micro- and immunobiologists from the Dartmouth Geisel School of Medicine, Yale University, and the University of Pittsburgh has found evidence suggesting that future research teams planning to use bacteriophages ...