Multilayer magnetic recording to realize high-density hard disk drives
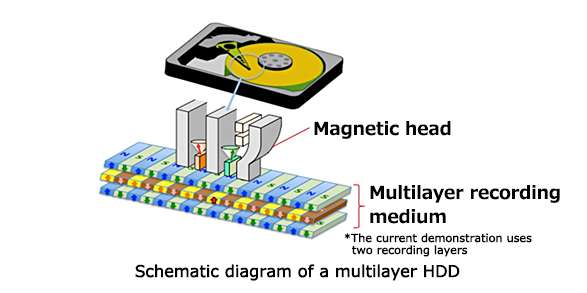
Researchers at Toshiba have demonstrated a new technology in which microwave magnetic fields are used to reverse magnetization directions by selecting layers in a multilayer magnetic medium. The developed magnetization reversal technology is expected to realize increased hard disk drive (HDD) capacity by adopting high-density, multilayer (three-dimensional) magnetic recording media.
With the spread of the Internet, the amount of information being created and exchanged worldwide has greatly increased. In the field of large-capacity storage technology, which is the foundation for accumulating and recording the information, magnetic recording technologies have become the mainstream technologies for inexpensively accumulating large amounts of information.
Magnetic recording technologies have conventionally increased the amount of information that can be stored per unit area by contracting recording bits. However, densification through the contraction is approaching the technical limits of recording density, so new high-density technologies are required. There is ongoing research for densification of solid-state storage memory technologies such as NAND through multilayering in addition to memory cell contraction. Researchers are also looking for ways to achieve multilayer structures in magnetic recording media, but until now there have been no proposed recording principles that would allow recording densities beyond the 10 Tb/in2 theoretical maximum allowed by contraction.
The researchers have demonstrated a new technology that adopts application of microwave magnetic fields to reverse the magnetization direction by selecting layers in a multilayer magnetic medium.
By stacking magnetic layers with different ferromagnetic resonance frequencies and applying a microwave field having a frequency corresponding to an appropriate ferromagnetic resonance, it is possible to excite a magnetization oscillation in only a specific magnetic layer. Magnetization reversal becomes possible in oscillation-excited layers, because the energy required for the magnetization reversal is reduced through a microwave assistance effect. While this technology has been previously predicted through simulation, this experiment represents its first realization. The magnetic reversal technology the researchers have demonstrated is a fundamental technology for magnetic recording, and can be applied to the multilayering (three-dimensional construction) of recording layers in HDDs, magnetic memory, magnetic tapes, and other high-density magnetic recording products.
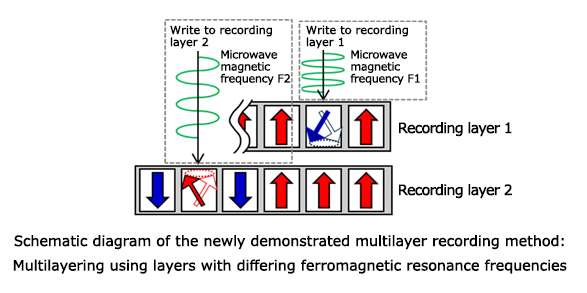
To allow for rewriting of small recording bits, they are currently developing a spin torque oscillation element to which localized microwave magnetic fields can be applied. They are also working toward the development of optimized recording media for multilayer recording.
Provided by Toshiba Corporation