New 3-D Test Method for Biomaterials 'Flat Out' Faster
A novel, three-dimensional (3-D) screening method for analyzing interactions between cells and new biomaterials could cut initial search times by more than half, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and Rutgers University report in the new issue of Advanced Materials.
The technique, an advance over flat, two-dimensional screening methods, enables rapid assessment of the biocompatibility and other properties of materials designed for repairing—or even rebuilding—damaged tissues and organs.
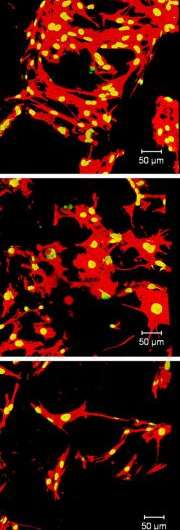
In what may be a first, the team demonstrated how to screen cell–material interactions in a biologically representative, but systematically altered, 3-D environment. The pivotal step in the experiment was the collaborators’ success in making so-called libraries of miniature porous scaffolds that are bone-like in structure but vary incrementally in chemical composition. Knowing how changes in scaffold ingredients influence cell responses, researchers can devise strategies for developing biomaterials optimized for particular therapies and treatments.
Until now, attempts to accelerate screening of candidate biomaterials have used flat films and surfaces. Along with other shortcomings, these two-dimensional substrates are neither consistent with cells’ normal 3-D environment inside the body nor with the most common intended use of biomaterials: creating scaffolds to encourage the growth of cells into functional 3-D tissues and organs.
“Cells are very sensitive to the texture, shapes, and other three-dimensional features of their local environment inside the body,” explains NIST biomaterial scientist Carl Simon. “The large difference in structure between 2-D films and 3-D scaffolds should be considered when screening new materials.”
On a series of plates, each about the size of a dollar bill and arrayed with 96 scaffolds the size of pencil erasers, the researchers conducted the equivalent of 672 individual tests. In all, the tests yielded data for eight separate but related investigations, each one using libraries of 36 incrementally varying scaffolds and 12 controls. On each plate, tests were performed concurrently.
The six cell-culture investigations and two studies of scaffold structure were completed in six days, as compared with 24 days for the traditional method of preparing and testing each sample individually.
In the cell culture experiments, the team analyzed how variations in the chemical makeup of the tiny scaffolds affected the ability of bone-building cells called osteoblasts to multiply and to adhere to scaffolds. The scaffold libraries were made by blending varying proportions of two different compounds prepared at Rutgers based on the amino acid tyrosine, which is a component of proteins found in hair, skin, and other parts of the body.
The project yielded a unique data set, where two materials have been tested side by side in both 2-D and 3-D. In this case, results with 2-D films were predictive of the trends observed with 3-D scaffolds. Further work is required to determine if this will hold true for other cell-material systems.
Citation: Y. Yang, M. L. Becker, D. Bolikal, J. Kohn, D. N. Zeiger and C. G. Simon, Jr. Combinatorial polymer scaffold libraries for screening cell-biomaterial interactions in 3-D. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20, 1–7.
Source: National Institute of Standards and Technology