India's capital grapples with toxic winter air pollution

Even for a city considered one of the world's most polluted, the Indian capital hit a new low this past week.
Air so dirty you can taste and smell it; a gray haze that makes a gentle stroll a serious health hazard.
According to one advocacy group, government data shows that the smog that enveloped New Delhi was the worst in the last 17 years. The concentration of PM2.5, tiny particulate pollution that can clog lungs, averaged close to 700 micrograms per cubic meter. That's 12 times the government norm and a whopping 70 times the WHO standards.
The Delhi winter, once a glorious time of clear—crisp days that meant holidays and weekends spent picnicking in its many public parks—is now a time of annual health woes.
As millions struggle with hacking coughs and burning eyes, many schools across the city have either shut down or ended all outdoor activities. Doctors have asked people to stay indoors during the worst days.
Yet many of the problems that turn Delhi's air so toxic continue unabated. People still set off massive amounts of festival fireworks, piles of garbage burn all night and dust from the construction projects that dot the city is unchecked.
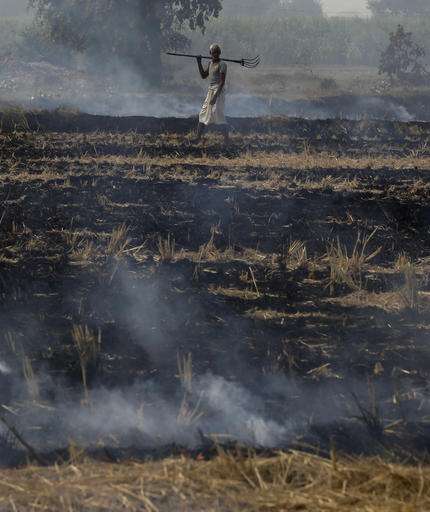

And at the start of every winter, farmers in the states bordering the city begin burning straw from their rice paddy crop to clear the fields for planting wheat.
"Sources of pollution in Delhi and outside of Delhi have exponentially increased in the last couple of days," said Polash Mukerjee, a research associate with the Centre for Science and Environment, a Delhi-based research and lobbying organization.
He said that wind direction is blowing toward Delhi from all directions, especially from Punjab and Haryana, "where there are large incidences of crop fires that we are detecting even today."
Over the last two years, the government has tried a slew of measures to control air pollution, including stricter emission norms for cars and a tax on diesel-fueled trucks that enter the city.

New Delhi also has attempted to limit the number of cars during the winter months, when air quality is at its worst. Twice the city imposed a two-week period in which cars were allowed on the roads only on even or odd days, depending on the vehicle's license plate number.
Last month, the city launched a smartphone application called "Change the Air," inviting residents to send photos and complaints about sources of pollution, from the burning of leaves and garbage in public parks to construction crews working without dust control measures.
But despite announcing new measures, the city has struggled with enforcing them on a regular basis.
One of the biggest struggles is crop burning in neighboring areas, where despite attempting to impose cash fines on farmers enforcement has been hard. For the farmers, it's cheaper to burn rice paddy straw than hire people to carry it away.

"Pollution is also caused by diesel cars, factories and many other sources. Farmers only do this for one month of the year," Bijendar Singh, a farmer in neighboring Haryana state, said as he watched his paddy straw burn.
"It is a compulsion for farmers to do this. Because of this compulsion, we spread air pollution. As much as it harms the people sitting in Delhi, it harms us and our children even more," he said.
Mukerjee, the research associate, said that the government hasn't worked out a strategy to help farmers dispose of their crop waste.
"Paddy straw that lies in your field today, as a farmer, it is absolutely worthless to me. I don't earn anything out of it. Why should I spend money collecting it?" Mukherjee said.
-

In this Friday, Nov. 4, 2016 photo, Bijender Singh walks through smoke caused by setting his field on fire to prepare it for its next yield at Chandhat, in the state of Haryana, south of New Delhi, India. Even as the Indian capital hit a new low on air pollution, many of the problems that turn Delhi's air so toxic continue unabated, like farmers in bordering regions continuing to burn crop waste. (AP Photo/Saurabh Das) -

A shopkeeper adjusts the face mask against air pollution of an Indian woman after she purchased it in New Delhi, India, Friday, Nov. 4, 2016. A new report from UNICEF says about a third of the 2 billion children in the world who are breathing toxic air live in northern India and neighboring countries, risking serious health effects including damage to their lungs, brains and other organs. New Delhi's air pollution is among the world's worst, spikes every winter because of the season's weak winds and countless garbage fires. Officials also said that the high pollution levels were made worse by the ongoing burning of spent crops in agricultural fields in the neighboring states of Punjab and Haryana.(AP Photo/Altaf Qadri) -
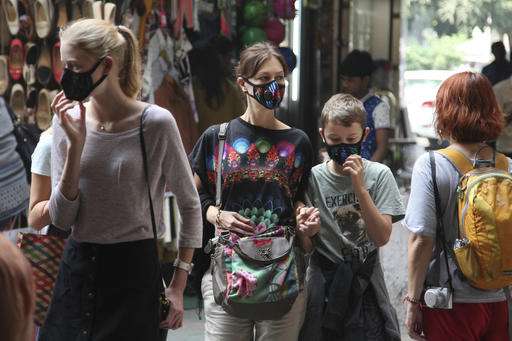
Foreigners walk at a market place wearing face masks against air pollution in New Delhi, India, Friday, Nov. 4, 2016. A new report from UNICEF says about a third of the 2 billion children in the world who are breathing toxic air live in northern India and neighboring countries, risking serious health effects including damage to their lungs, brains and other organs. New Delhi's air pollution is among the world's worst, spikes every winter because of the season's weak winds and countless garbage fires. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri) -

An Indian woman talks to another wearing a face mask against air pollution at a shop in New Delhi, India, Friday, Nov. 4, 2016. A new report from UNICEF says about a third of the 2 billion children in the world who are breathing toxic air live in northern India and neighboring countries, risking serious health effects including damage to their lungs, brains and other organs. New Delhi's air pollution is among the world's worst, spikes every winter because of the season's weak winds and countless garbage fires. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri) -

A child puts on a face mask inside a shop selling face masks against air pollution in New Delhi, India, Friday, Nov. 4, 2016. A new report from UNICEF says about a third of the 2 billion children in the world who are breathing toxic air live in northern India and neighboring countries, risking serious health effects including damage to their lungs, brains and other organs. New Delhi's air pollution is among the world's worst, spikes every winter because of the season's weak winds and countless garbage fires. Officials also said that the high pollution levels were made worse by the ongoing burning of spent crops in agricultural fields in the neighboring states of Punjab and Haryana. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri) -

Customers crowd as they wait for their turn to buy face masks against air pollution in New Delhi, India, Friday, Nov. 4, 2016. A new report from UNICEF says about a third of the 2 billion children in the world who are breathing toxic air live in northern India and neighboring countries, risking serious health effects including damage to their lungs, brains and other organs. New Delhi's air pollution is among the world's worst, spikes every winter because of the season's weak winds and countless garbage fires. Officials also said that the high pollution levels were made worse by the ongoing burning of spent crops in agricultural fields in the neighboring states of Punjab and Haryana. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
© 2016 The Associated Press. All rights reserved.