Image: Boulders on a Martian landslide
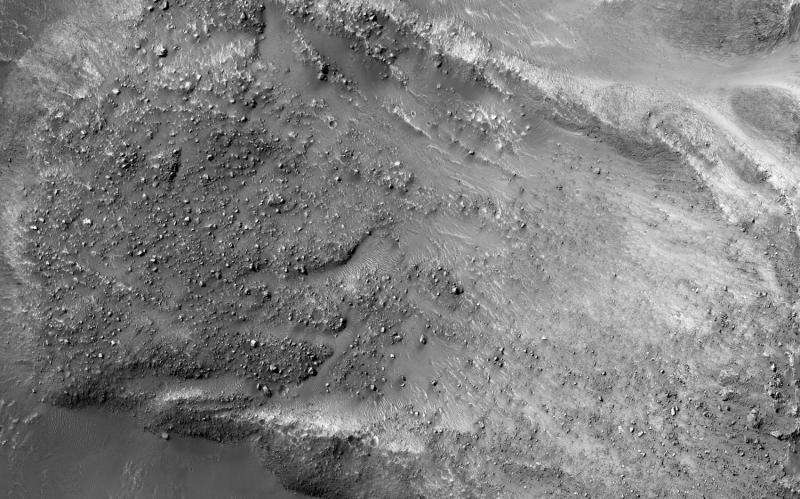

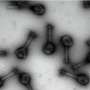
The striking feature in this image, acquired by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on March 19, 2014, is a boulder-covered landslide along a canyon wall. Landslides occur when steep slopes fail, sending a mass of soil and rock to flow downhill, leaving behind a scarp at the top of the slope. The mass of material comes to rest when it reaches shallower slopes, forming a lobe of material that ends in a well-defined edge called a toe.
This landslide is relatively fresh, as many individual boulders still stand out above the main deposit. Additionally, while several small impact craters are visible in the landslide lobe, they are smaller in size and fewer in number than those on the surrounding valley floor. The scarp itself also looks fresh compared to the rest of the cliff: it, too, has boulders, and more varied topography than the adjacent dusty terrain.
Just to the north of the landslide scarp is a similarly-shaped scar on the cliffside. However, there is no landslide material on the valley floor below it. The older landslide deposit has either been removed or buried, a further indicator of the relative youth of the bouldery landslide.
Provided by NASA