Fast folding for synthetic peptides and microproteins
Certain types of peptides and microproteins for drug discovery research can be made more efficiently and quickly using a reaction solvent that helps mimic nature's way.
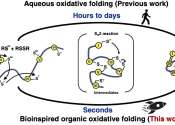
Certain types of peptides and microproteins for drug discovery research can be made more efficiently and quickly using a reaction solvent that helps mimic nature's way.
Biochemistry
Mar 22, 2024
0
0

An international team of astronomers including UCL's (University College London's) Professor Mike Barlow has discovered the first conclusive evidence that a neutron star exists at the center of Supernova 1987A, a star explosion ...
Astronomy
Feb 22, 2024
1
410

Within the bread, rolls and baked goods on many tables this holiday season is an extraordinary substance—gluten. Gluten's unique chemistry makes foods airy and stretchy.
Other
Nov 21, 2023
0
19

When it comes to chemical reactions, fluorine has a reputation as a 'magic bullet atom' for its ability to increase a drug's absorption and prolong its lifetime. However, traditional methods of adding it to compounds entail ...
Biochemistry
Nov 13, 2023
0
16

Oxygen plays a crucial role for all living organisms on Earth. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have now found evidence that double ionized sulfur dioxide contribute to the formation of oxygen molecules. This could, ...
Analytical Chemistry
Oct 12, 2022
0
10

Scientists using sophisticated computational chemistry techniques have identified a new pathway for how sulfur particles can form in the atmosphere of Venus. These results may help to understand the long sought-after identity ...
Planetary Sciences
Aug 9, 2022
0
319

A team of researchers at the California Institute of Technology's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, working with a colleague from the University of Edinburgh, has found evidence suggesting that the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai eruption ...

Nitrogen, an element that is essential for all living cells, makes up about 78 percent of Earth's atmosphere. However, most organisms cannot make use of this nitrogen until it is converted into ammonia. Until humans invented ...
Materials Science
May 27, 2021
0
136

In a number of biological processes, iron–sulfur clusters play a vital role, where they act as cofactors to enzymes. Research published in Angewandte Chemie now shows that cubic clusters can support unusual bonding states. ...
Analytical Chemistry
May 3, 2021
0
19

Copper remains one of the single most ubiquitous metals in everyday life. As a conductor of heat and electricity, it is utilized in wires, roofing and plumbing, as well as a catalyst for petrochemical plants, solar and electrical ...
Materials Science
Apr 24, 2021
5
1848