New study reveals how parasites shape complex food webs
A new study published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences sheds light on how parasites influence the intricate relationships between predator and prey populations.

A new study published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences sheds light on how parasites influence the intricate relationships between predator and prey populations.
Ecology
Apr 24, 2024
0
1
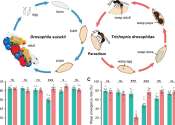
A parasitic wasp that preys on the young of a prolific fruit fly pest demonstrates both molecular evolution and behavioral adaptations in the face of ecological pressures, according to new research.
Plants & Animals
Apr 23, 2024
0
57

Did you know that the world's deadliest animal is the mosquito? And Aedes aegypti is one of the most dangerous. This bug spreads viruses that cause dengue fever, which was recently declared as an epidemic in Puerto Rico.
Molecular & Computational biology
Apr 8, 2024
0
22

A recent breakthrough sheds light on how the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, invades human red blood cells. The study, led by the Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute (Swiss TPH) and Griffith University's Institute ...
Cell & Microbiology
Apr 3, 2024
0
0

A mysterious parasite from Asia is infecting snakes over most of Florida, and researchers believe it was likely brought here by invasive Burmese pythons.
Plants & Animals
Apr 3, 2024
0
0

Bacteria that could help one of Africa's staple crops resist a major pest have been identified by researchers at the University of California, Davis. Their findings, published in Cell Reports, could improve yields of sorghum, ...
Cell & Microbiology
Mar 27, 2024
0
41

Researchers from the Max Planck Institutes (MPI) for Evolutionary Biology in Plön and for Biology in Tübingen have made significant progress in understanding the evolution of interactions between plants and microbes. The ...
Evolution
Mar 13, 2024
0
1

By dissecting the genetic diversity of the most deadly human malaria parasite—Plasmodium falciparum—researchers at EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) have identified a mechanism of 'copy-paste' genetics ...
Evolution
Mar 7, 2024
0
88

Researchers with the University of Minnesota hope to release highly specialized parasitic wasps to serve as a biological control method to save Darwin's finches from a dire threat: the invasive avian vampire fly, Philornis ...
Plants & Animals
Mar 5, 2024
1
25

Whether you're a gardener growing food for your household, a small-scale farmer or a commercial producer, soil matters. You cannot really tell the difference between healthy and unhealthy soil just by looking at it. But there ...
Ecology
Mar 5, 2024
0
0
Parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between two different organisms where one organism, the parasite, takes favor from the host, sometimes for a prolonged time. In general, parasites are much smaller than their hosts, show a high degree of specialization for their mode of life, and reproduce more quickly and in greater numbers than their hosts. Classic examples of parasitism include interactions between vertebrate hosts and diverse animals such as tapeworms, flukes, the Plasmodium species, and scabs. Parasitism is differentiated from parasitoidism, a relationship in which the host is always killed by the parasite such as moths, butterflies, ants, flies and others.
The harm and benefit in parasitic interactions concern the biological fitness of the organisms involved. Parasites reduce host fitness in many ways, ranging from general or specialized pathology (such as castration), impairment of secondary sex characteristics, to the modification of host behaviour. Parasites increase their fitness by exploiting hosts for food, habitat and dispersal.
Although the concept of parasitism applies unambiguously to many cases in nature, it is best considered part of a continuum of types of interactions between species, rather than an exclusive category. Particular interactions between species may satisfy some but not all parts of the definition. In many cases, it is difficult to demonstrate that the host is harmed. In others, there may be no apparent specialization on the part of the parasite, or the interaction between the organisms may be short-lived. In medicine, only eukaryotic organisms are considered parasites, with the exclusion of bacteria and viruses. Some branches of biology, however, regard members of these groups as parasitic.[citation needed]
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA