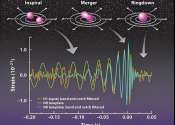
Astrophysicists uncover supermassive black hole/dark matter connection in solving the 'final parsec problem'
Researchers have found a link between some of the largest and smallest objects in the cosmos: supermassive black holes and dark matter particles.