This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Novel universal principle guides properties of fluorophosphate glass
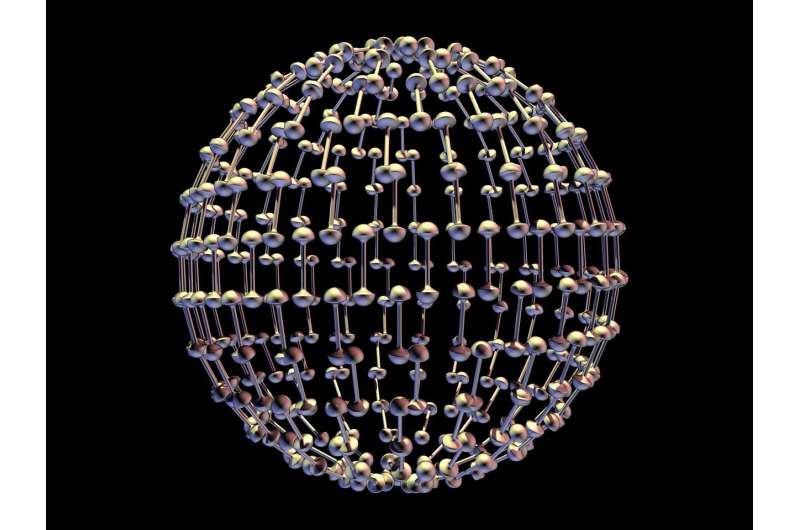
A research team led by Prof. Wang Pengfei from Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (XIOPM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed the relationship between F/O ratio and the structure of fluorophosphate glass through conducting comprehensive research on Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
The results were published in the Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids.
The performance of fluorophosphate glass is closely related to its structure. However, the conclusions drawn from all the studies on the structure of fluorophosphate glass so far cannot be universally applied to glasses with different components.
Given that F- and O- are the only two existing anions and play a dominant role in the structure, studying the common structural features of glasses based on F/O ratio is an efficient approach.
In this study, researchers prepared a series of glass samples based on the fluorophosphate system with an F/O ratio range of 1 to 7. They studied the content changes of different Qn groups under different F/O ratio by Raman and NMR spectra. Then, they concluded quantitative relationship between F/O ratio and Qn characteristics through comparative analysis of reported NMR spectra.
When the F/O ratio is below 0.3, Q2 content is highest, while the unit presence of Q0 is very small, and the percentage is less than 10%. When the F/O ratio is in the range of 0.3 to 1, the Qn units with the highest content is composed of Q2 or Q1 units.
With the increase of the F/O ratio, the content of Q1 increased significantly, while the content of Q0 remained relatively stable within this range. When the F/O ratio is in the range of 1 to 4, the Qn units with the highest content include Q0 or Q1 units.
When the F/O ratio is more than 4, the Qn units with the highest content are composed of Q0. With the increase of oxygen content ratio, the growth rate of Q0 slows down and approaches saturation.
This study reveals the general rule of the effect of F/O ratio on the structure of fluorophosphate glass, which provides an effective way to predict the structure and properties of glass by composition.
More information: Xin Cao et al, Structural insight of fluorophosphate glasses through F/O ratio: Case study of Raman and NMR spectra, Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2024.123065
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences