This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Mongolians fight plastic pollution in vast steppe
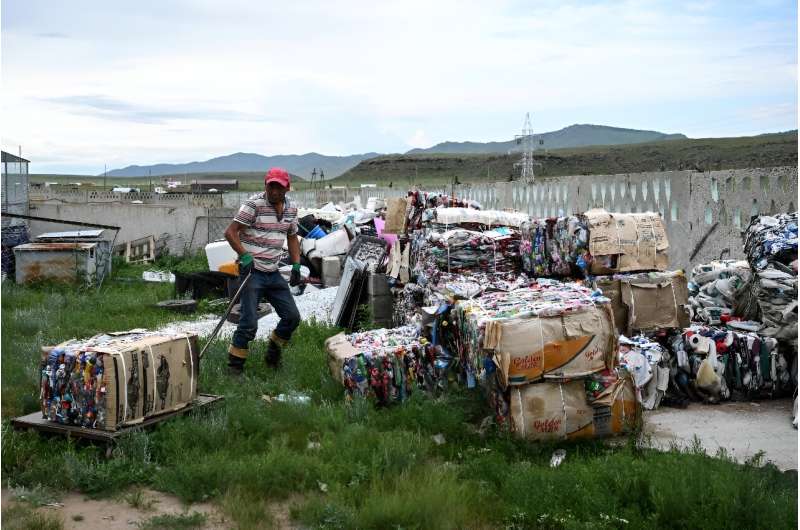

Mongolian herder Purev Batmunkh sighs as he picks through waste strewn across a field—the refuse of an unsightly and deadly waste pollution problem affecting swathes of the steppe.
His country is among the world's top per capita producers of plastic waste, and without a centralized recycling program, campaigners say some 90 percent of it ends up in landfills.
"Most people live in the moment and they don't really think about the future and just throw their garbage," Batmunkh told AFP in the Khishig-Undur district of Mongolia's northern Bulgan province.
"They don't know how long this garbage will stay, for how many years."
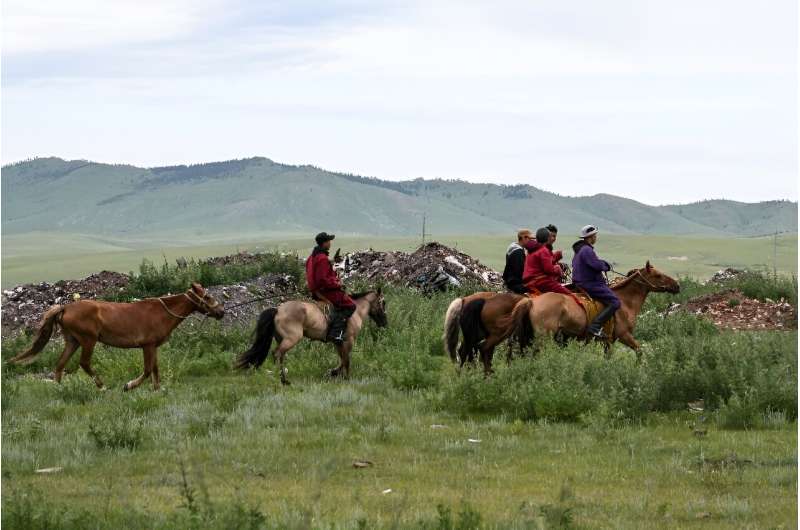
Illegal dumping is common and some of it then blows into pastoral lands, where it is eaten by livestock.
Batmunkh said one of his cows had been "drooling and could not really move".
"A few days passed and it died," he said.
"We gutted the cow and we found that all the way from its neck to its intestines and bladder, there was a plastic raincoat inside it."
Mongolia introduced a ban on single-use plastic bags in 2019.
But in the steppe, it appears to have had little effect.
In a nearby field, a mountain of multicolored plastic waste, from fizzy drink bottles to tires and shopping bags, lies festering just a few meters from where the horses graze.

'Zero-waste'
Annual plastics production worldwide has more than doubled in 20 years to 460 million tonnes, and is on track to triple within four decades if left unchecked.
Only nine percent is recycled, and according to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, its contribution to global warming could more than double by 2060—having accounted for 3.4 percent of global emissions in 2019.
But, in rural Mongolia, some are trying to help.
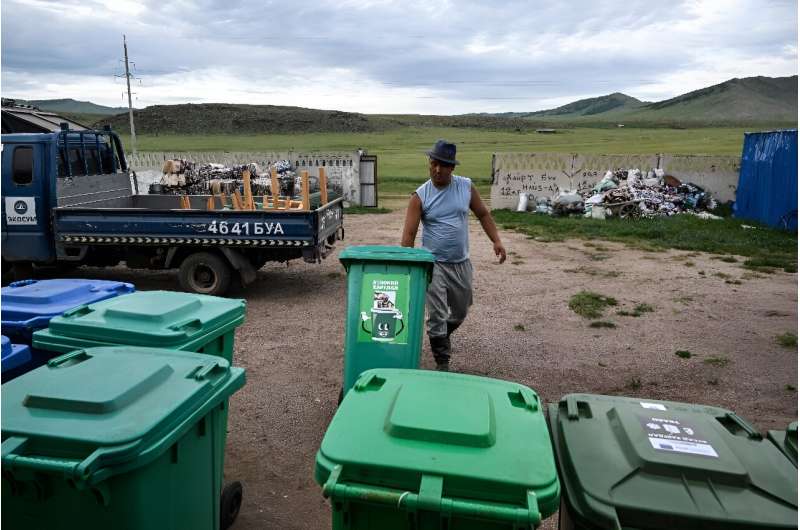
Since 2018, local NGO Ecosoum has organized one of the area's first recycling facilities—encouraging herders and others to pick up local waste and bring it to them for processing.
Partially funded by the European Union, it is seeking to turn Khishig-Undur into Mongolia's first "zero-waste" district.
"These kinds of plastics are all over Mongolia," Batkhuyag Naranbat, technical coordinator at the recycling facility, told AFP, columns of processed bottles piled high behind him.
"Livestock go out and eat these plastics and even die eating plastic," he said.

"We need to stop."
For Naranbat, work starts bright and early, when he and his colleagues head out to collect waste from those who can't bring it to the facility themselves.
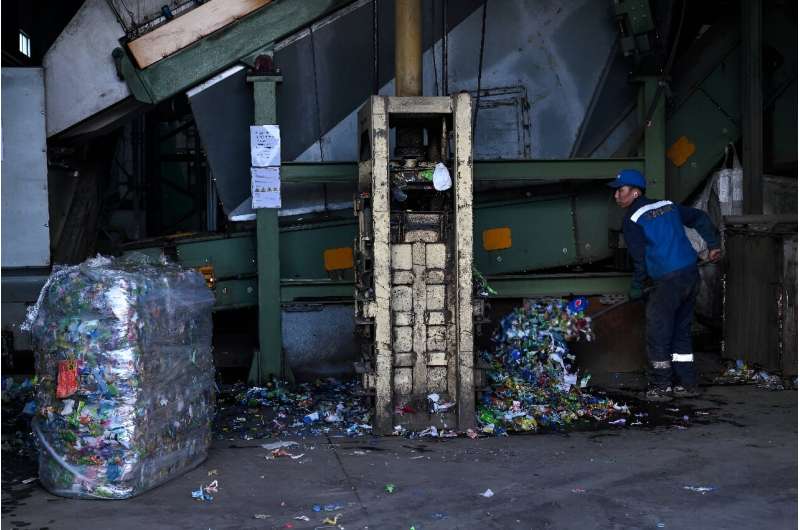
They then separate the plastics into what can be re-used and what can't.
The plastic is then pressed into one-ton cubes, placed on a truck and sent to the capital Ulaanbaatar for processing.
People in the areas used to dump plastic in giant pits or burn it, Naranbat said.
"But when we learned about how this plastic pollution is detrimental, not only for the world but for our own country, we asked: 'what have we done?'" he said.
"We are the ones who caused the problem, we should be the ones to solve the issue."
Herder Batmunkh, who is 58, also decided to help, heading out on his horse every week to scour the steppe for rubbish to pick up and deliver to Ecosoum.
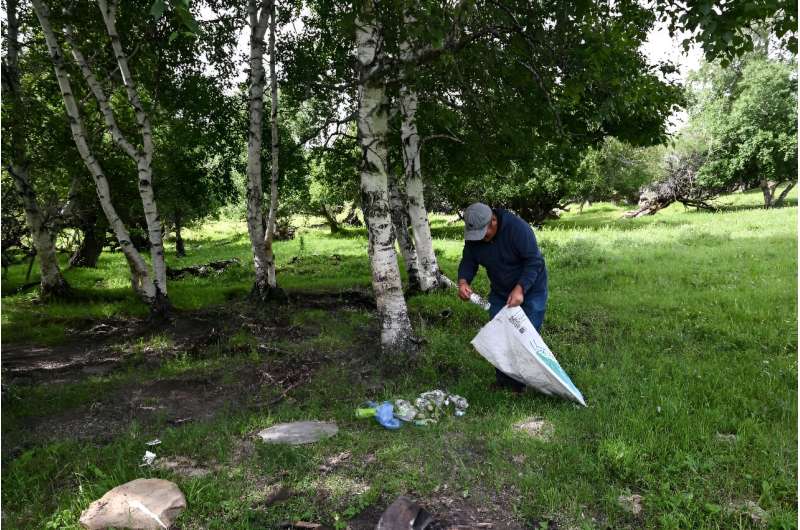

"While I'm herding, I'll spot a bit of garbage and I'll put it in the bag that I have," he said.
His diligence hasn't always made him friends.
"When I tell my neighbors to take care of the garbage, they mock me and say, 'Batmunkh rambles on about nonsense,'" he said.
"They don't care."
'Large companies' to blame
While individual habits need to change, Naranbat said the companies that produce the plastic must be held accountable.
"They need to change and start using other forms of material, like aluminum—those things are recyclable," he said.
A fourth and penultimate round of UN-led negotiations on a world-first pact to solve global plastic pollution wrapped up in Canada in April.
Talks are set to conclude in November in South Korea, though a proposed cap on plastic production did not make it into the draft text and remains a major sticking point.

But Batmunkh said he felt everyone needed to play a role in helping make Earth a better place.
"The things that separate us from animals is our rationality –- that makes us human," he said, his young grandson, hanging on his every word, pulling on his arm.
"As humans who are living on this Earth, all of us need to bear the responsibility of caring for our planet."
© 2024 AFP