This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
proofread
Threatened urban wetlands play a crucial role in biodiversity and sustainability, says study

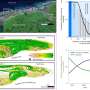
Researchers at the University of Helsinki have studied and documented the historical transformation of the urban wetlands and ponds in the Helsinki region from the 19th century to the present. Based on their findings, historical urban wetlands can be divided into three categories:
- completely destroyed wetlands that have been entirely obliterated due to urbanization and land-use changes
- ecologically destroyed wetlands that have undergone significant ecological degradation
- wetlands that have managed to retain their ecological functionality.
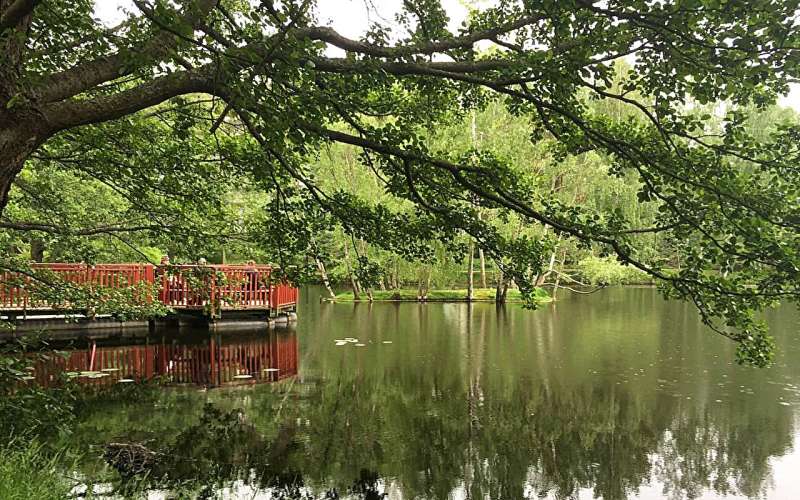
Urban wetlands play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity, regulating the climate and enhancing urban sustainability. As cities face climate change and increased urbanization, preserving and rehabilitating these wetlands is crucial for mitigating environmental challenges and enhancing residents' quality of life.
Based on the historical evaluation, the researchers found that population growth, urbanization, industrialization, land-use change and climate change are the most significant factors threatening wetland ecosystems over time. These factors are interconnected and influence each other.
Rapid population growth, urbanization and industrialization have strained urban wetlands. Termed land-use change, this transformation involves draining, shrinking or converting urban wetlands into various landscapes, ultimately leading to the destruction of wetlands and their biodiversity.
This directly impacts wetland vegetation, altering flora, compromising hydrology and threatening biodiversity. Additionally, soil alterations, like asphalt and concrete, disrupt water–substrate connections. Climate change, driven by high temperatures and precipitation, exacerbates eutrophication, depleting oxygen and causing biodiversity loss in Helsinki's urban wetlands.
"These findings emphasize the importance of effective policies and management practices to protect these ecosystems, given their role in biodiversity conservation, climate regulation and in enhancing residents' well-being," says main author Somayeh Alikhani from the University of Helsinki.
According to Alikhani, the results are significant, as they shed light on the historical context and evolution of urban wetlands. It helps raise awareness among the community about the changes that have taken place in these wetlands over time.
"This study highlights the importance of valuing and conserving urban wetlands for their ecological and societal benefits," Alikhani says. The research is published in the journal Wetlands.
Informed decision-making for urban planners
According to Alikhani, the results of the study can be used, for example, to plan the management and restoration of existing wetlands. The research also helps policymakers and city planners make informed decisions that enhance urban sustainability, making cities more livable and resilient. It also serves as a foundation for further research into urban sustainability and resilience.
"The environmental history analysis of urban wetlands fosters an understanding of the value of urban wetlands in the history and future of cities. It enables citizens to appreciate the ecological and recreational benefits of these areas and encourages their involvement in local conservation efforts. Also, this research raises awareness and instills a sense of responsibility in the public to protect and preserve these vital ecosystems for current and future generations," Alikhani concludes.
More information: Somayeh Alikhani et al, Modified, Ecologically Destructed, and Disappeared—History of Urban Wetlands in Helsinki Metropolitan Area, Wetlands (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s13157-023-01671-w
Provided by University of Helsinki