This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Grow-your-own households eat more fruit and vegetables while wasting less, research suggests
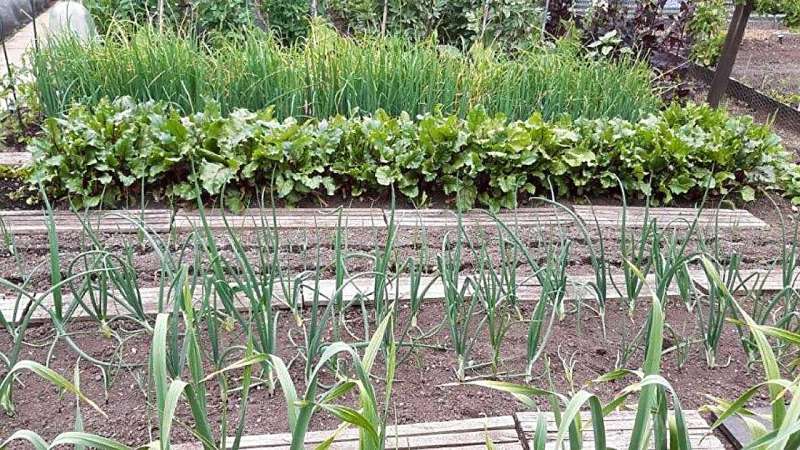

Household fruit and vegetable production, in allotments and gardens, could be key to a healthy and food-secure population, a new study from the University of Sheffield has found.
The study followed household food-growers over the course of a year to assess their production, purchase, donation and waste of fruit and vegetables.
It found those who grow their own can produce more than half of the vegetables (51%) and 20% of the fruit they consume annually.
As well as providing sustainable access to fresh fruit and vegetables, the study also found household food growers ate 6.3 portions of their recommended five-a-day, which is 70% higher than the UK national average at only 3.7 portions. This finding suggests household food production could promote the adoption of a healthier diet.
Author of the study, Dr. Zilla Gulyas, from the University of Sheffield's School of Biosciences, said, "Eating at least five portions of fruit and vegetables a day is associated with significantly decreased risks of developing health issues like obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer, and could help prevent associated deaths and cut health care costs worldwide.
"Our new study highlights the role that growing fruit and vegetables at a household scale could play in increasing their consumption."
The findings of the study suggest that household food production could both promote fruit and vegetable consumption and play an important role in increasing household and national food self-sufficiency, as well as reducing waste. The findings are published in the journal Plants, People, Planet.
Households that had the ability to grow their own fruits and vegetables also wasted little, with only 0.12 portions a day being thrown out on average. This is 95% lower than the fruit and vegetable waste of the average UK household.
This suggests that household food production was associated with more waste-reducing behaviors which could also increase household food security on a national scale, as participants commonly engaged in behaviors like donating unneeded food items and persevering and freezing excess food for later use.
According to the National Food Strategy published in 2021, developing the ability of the national food system to provide sufficient amounts of healthy food for all, while withstanding socio-economic and environmental shocks, and pressures from continued rapid urbanization and climate change, is a key priority in the UK. Although, the role of own-growing in this was overlooked and going forward should be recognized in government policy.
Dr. Gulyas states household level food production could play an important role in promoting both healthy diets and food system resilience. For this however, people need better access to space and other resources needed to grow their own.
She said, "We need to find ways to overcome socio-economic challenges to upscaling household food production, especially among those most affected by low fruit and vegetable intakes, like low-income families. Increasing the amount of space available to UK households to produce their own food is essential to this, especially given the steady decline in allotment land nationally."
Dr. Jill Edmondson, from the University of Sheffield's School of Biosciences, said, "Global food security is one of the biggest challenges we will face in the future, therefore it's crucial that we find new ways to increase the resilience of the UK food system.
"This study provides the first long-term evidence that household food production could play in promoting healthier diets through self-sufficiency and adds important support to any policy making that seeks to expand household level fruit and vegetable production."
More information: Boglarka Z. Gulyas et al, The contribution of household fruit and vegetable growing to fruit and vegetable self‐sufficiency and consumption, Plants, People, Planet (2023). DOI: 10.1002/ppp3.10413
Journal information: Plants, People, Planet
Provided by University of Sheffield