This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
Maritime sector seals carbon-cutting deal but sparks criticism
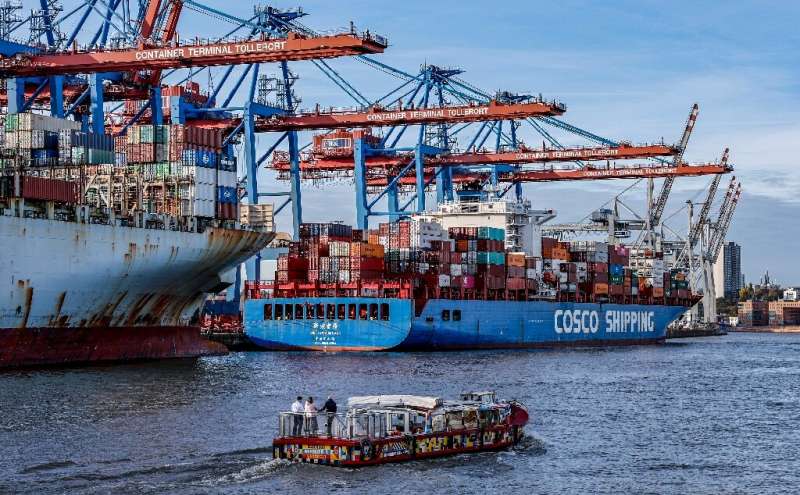

The International Maritime Organization, which oversees the highly polluting shipping industry, clinched a landmark deal on Friday to improve its target to cut carbon emissions—but green campaigners said it fell far too short to tackle climate change.
The London-based IMO said its Marine Environment Protection Commission has adopted a "historic... strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping".
The United Nations' global shipping regulator said nations had agreed to cut total annual emissions of greenhouse gases by at least 20 percent by 2030 and by at least 70 percent by 2040 compared to 2008 levels.
The revised strategy also aims for the industry to reach net-zero emissions "close to" 2050. That compared with the prior target for a 50-percent reduction by mid-century.
"IMO remains committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from international shipping and, as a matter of urgency, aims to phase them out as soon as possible," the agency said.
However, environmental non-governmental organizations slammed the agreement, arguing it was insufficient under the framework of the landmark Paris climate accord.
The green lobby instead wants the shipping sector to implement a 50-percent reduction by 2030 and deliver carbon neutrality by 2040.
"They knew what the science required, and that a 50-percent cut in emissions by 2030 was both possible and affordable," said John Maggs, president of the Clean Shipping Coalition.
"Instead, the level of ambition agreed is far short of what is needed to be sure of keeping global heating below 1.5 degrees Celsius, and the language seemingly contrived to be vague and non-committal."
The deal came at the end of a five-day meeting at the IMO's headquarters in London, attended by representatives from 100 countries involved in the shipping industry—which emits roughly the same level of greenhouse gases as aviation.
'Falls short'
The gathering pitted climate-vulnerable nations—particularly islands in the Pacific—and richer countries against big exporters like China.
The vast majority of the world's 100,000 cargo ships—which carry 90 percent of the world's goods—are powered by highly polluting diesel.
Shipping is responsible for around three percent of global greenhouse gas emissions, according to the United Nations.
The IMO said the "carbon intensity" of ships was expected to decline over time with "further improvement of energy efficiency" of new vessels.
But Harjeet Singh, head of global political strategy for Climate Action Network International, said the IMO's revised strategy "unfortunately falls short of expectations".
"There is a clear disparity between its goals and those set by the Paris agreement."
Greenpeace UK welcomed the deal but also declared it was "still too weak" to fight pollution in a sector which "has operated out of sight" for too long.
Under the 2015 Paris deal, nations pledged to reach net-zero carbon emissions by the middle of the century with the aspirational goal of limiting the increase in global temperatures to 1.5 C above pre-industrial levels.
Germany's representative Dieter Janecek said the agreement was "important" but cautioned the world would still have to focus on cutting pollution sufficiently to stop the planet heating by more than 1.5 C.
French oceans minister Herve Berville said the IMO deal was "a success" even though "we came to the negotiating table with stronger ambitions that what was achieved in the final agreement".
Inadequate
The European Union had wanted the shipping industry to set intermediate targets, not just a 2050 goal.
Those would have required the industry to start cutting pollutant carbon emissions right now, in order to achieve a 29-percent cut by 2030 and an 83-percent reduction by 2040.
Argentina, Brazil and China, in particular, had strongly resisted tougher IMO targets, arguing they cost poor, developing countries the most.
They are also strongly opposed to a flagship proposal for a global levy, or carbon tax, on shipping emissions.
French President Emmanuel Macron backed the idea at a recent climate finance summit in Paris but said it would need support from China, the United States and other European nations to work.
Green campaigners had protested on Monday outside the IMO in central London.
Several dozen activists, including some dressed as jellyfish, called for greener freight to help tackle climate change and protect the oceans.
The Clean Shipping Coalition argued on Friday that the regulator was simply not doing enough.
"This agreement is the latest example of a pattern of behavior at the IMO, where climate and environment issues are addressed but not adequately responded to," the coalition said.
"(It raises further questions about the institution's suitability as a venue for tackling shipping's serious impact on the climate and oceans," the NGO added.
© 2023 AFP