This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
reputable news agency
proofread
France to probe microplastic pellet pollution on Atlantic beaches

French prosecutors said on Friday they would investigate the appearance of vast quantities of tiny toxic plastic pellets along the Atlantic coast that endanger marine life and the human food chain.
The criminal probe will follow several legal complaints about the pellet invasion lodged by local authorities and the central government in Paris, Camille Miansoni, chief prosecutor in the western city of Brest, told AFP.
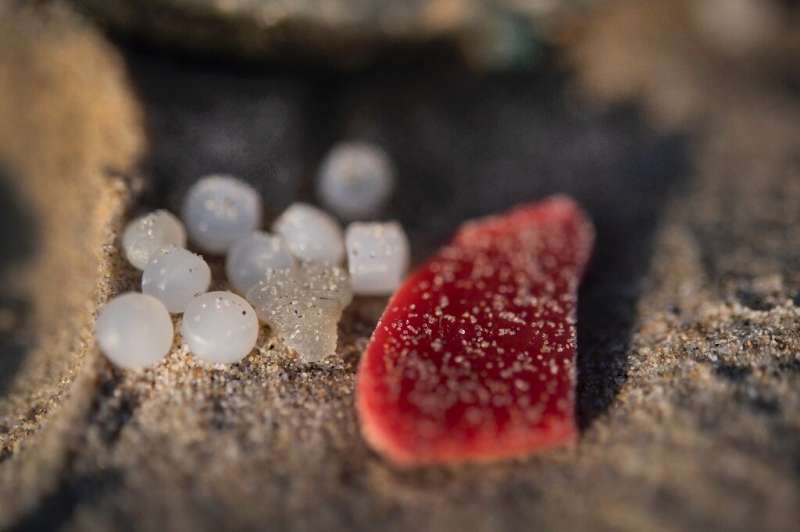
The microscopic pellets, called nurdles, are the building blocks for most of the world's plastic production, from car bumpers to salad bowls.
They are usually packed in bags of 25 kilogrammes (55 pounds) for transport, each containing around a million nurdles, which are sometimes called "Mermaids' Tears".
But they can easily spill into the ocean when a cargo ship sinks or loses a container. Environmentalists also suspect that factories sometimes dump them into the sea.
Fish and birds often mistake them for food and, once ingested, the tiny granules can make their way into the diet of humans.
Experts told AFP the nurdles found along the coast of Brittany may have come from a plastic industry container that fell into the sea.
"We can't rule out a single source for the industrial pellets," said Nicolas Tamic at the CEDRE pollution research body in Brest.
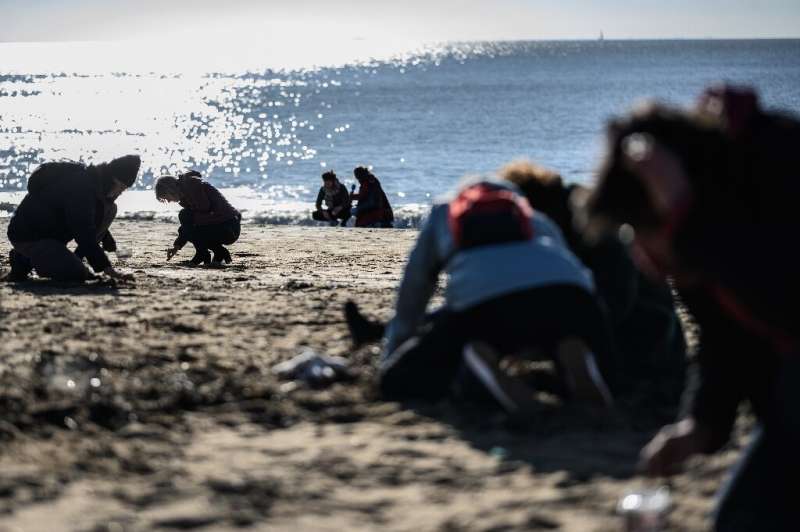

On Tuesday, the French government filed a legal complaint against persons unknown and called for a international search for any containers that may have been lost at sea.
Local authorities have followed suit, and the environmental crime branch of the Brest prosecutor's office will lead the investigation.
Last weekend, around 100 people took part in a clean-up campaign on a microplastic-infested beach in Pornic in Brittany to collect pellets and draw attention to the problem.
"We think they've come from a container that may have been out there for a while and opened up because of recent storms," said Lionel Cheylus, spokesman for the NGO Surfrider Foundation.
"Our action is symbolic. It's not like we're going to pick up an entire container load," said Annick, a pensioner, as she filled her yoghurt pot with nurdles.
French politicians have taken note. Joel Guerriau, a senator from the region, has called for a "clear international designation" of the pellets as being harmful.
Ecological Transition Minister Christophe Bechu labelled the nurdles "an environmental nightmare", telling AFP the government would support associations fighting pellet pollution.
Ingesting plastic is harmful for human health but nurdles, in addition, attract chemical contaminants found in the sea to their surface, making them even more toxic.
Measuring less than five millimetres (0.2 inches) in size, they are not always readily visible except when they wash up in unusually huge quantities, as has been the case since late November along the northwestern French coast.
© 2023 AFP