Gravitational self-lensing of massive black hole binaries

A "massive" black hole (MBH) is one whose mass is more than about one hundred thousand solar-masses. MBHs reside at the centers of most galaxies, and when they actively accrete gas and dust onto their surrounding hot disk environments they radiate across the electromagnetic spectrum and are classified as active galactic nuclei.
Most galaxies have been involved in a merger with another galaxy during their lifetimes (indeed, these interactions are an important phase in galaxy evolution), and when they merge their two MBHs can form a binary system, orbiting one another. Such binaries are rare, however; theoretical estimates are that only about one active galaxy in a thousand will host a binary MBH.
Still, astronomers think finding binary MBHs is possible. Binary MBHs are promising sources of gravitational waves that should be detectable as they travel past pulsars by the way they distort the timing of pulsars' precise pulsed radio emission. Additionally, binary MBHs that accrete material are predicted to emit faint electromagnetic signals across the spectrum. But so far neither of these effects has been spotted and no binary MBHs have been definitively detected.
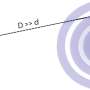
CfA astronomer Rosanne DiStefano and her colleagues have identified a third method to spot binary BMHs using a technique that Di Stefano and her colleagues first suggested in 2018. They propose looking for variability in the optical signal due to the gravitational lensing, by the MBHs, of light emitted by accreting material in their surrounding disk.
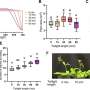
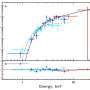
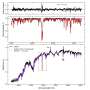
Variable light curves have been successfully used to detect gravitational lensing from exoplanets, for example, as they distort the light from a background star. The scientists use the Illustris computer simulation of galaxy evolution to estimate the frequency, orientation, accretion, and other properties of binary MBHs. The astronomers predict, based on the capabilities of the Rubin Observatory Legacy Survey of Space and Time survey, that between ten to one hundred gravitationally self-lensed binary MBHs could be positively detected, even after accounting for numerous complicating effects like dust obscuration or intrinsic AGN variability. The results would be significant, not only helping to prove the existence of binary MBH systems, but also in studying the orbital parameters of these objects and their accretion activity.
The research was published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
More information: Luke Zoltan Kelley et al, Gravitational self-lensing in populations of massive black hole binaries, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2021). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stab2776
Journal information: Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
Provided by Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian