Nature pushed to the brink by 'runaway consumption'

Unbridled consumption has decimated global wildlife, triggered a mass extinction and exhausted Earth's capacity to accommodate humanity's expanding appetites, the conservation group WWF warned Tuesday.
From 1970 to 2014, 60 percent of all animals with a backbone—fish, birds, amphibians, reptiles and mammals—were wiped out by human activity, according to WWF's "Living Planet" report, based on an ongoing survey of more than 4,000 species spread over 16,700 populations scattered across the globe.
"The situation is really bad, and it keeps getting worse," WWF International director general Marco Lambertini told AFP.
"The only good news is that we know exactly what is happening."
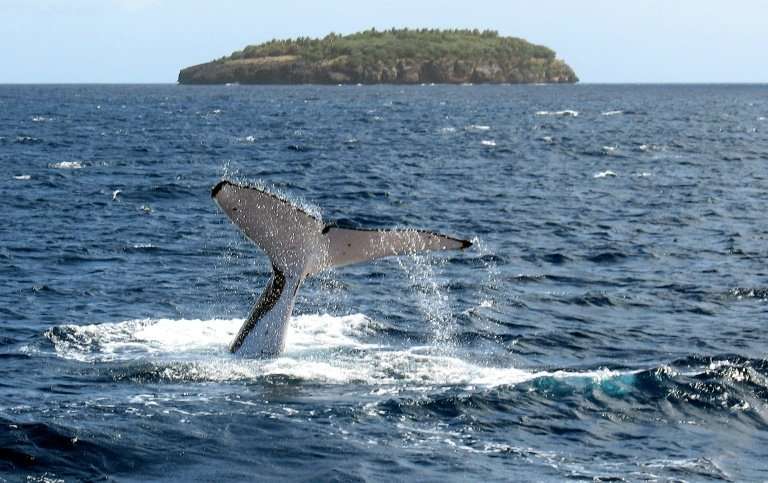
For freshwater fauna, the decline in population over the 44 years monitored was a staggering 80 percent. Regionally, Latin America was hit hardest, seeing a nearly 90 percent loss of wildlife over the same period.
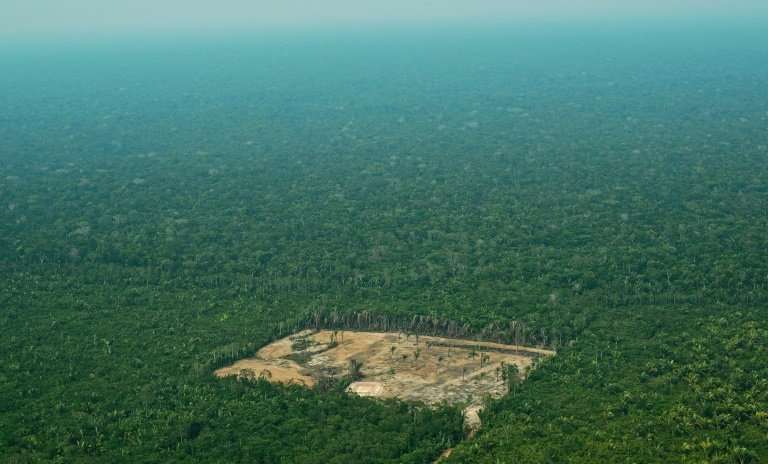
Another dataset confirmed the depth of an unfolding mass extinction event, only the sixth in the last half-billion years.
Depending on which of Earth's lifeforms are included, the current rate of species loss is 100 to 1,000 times higher than only a few hundred years ago, when people began to alter Earth's chemistry and crowd other creatures out of existence.
Measured by weight, or biomass, wild animals today only account for four percent of mammals on Earth, with humans (36 percent) and livestock (60 percent) making up the rest.
The great acceleration
Ten thousand years ago that ratio was probably reversed.

"The statistics are scary," said Piero Visconti, a researcher at the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis in Austria and one of 59 co-authors of the 80-page report.
"Unlike population declines, extinctions are irreversible."
For corals, it may already be too late.
Back-to-back marine heatwaves have already wiped out up to half of the globe's shallow-water reefs, which support a quarter of all marine life.
Even if humanity manages to cap global warming at 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit)—mission impossible, according to some scientists—coral mortality will likely be 70 to 90 percent.
A 2C world would be a death sentence, a major UN report concluded last month.
Half-a-century of conservation efforts have scored spectacular successes, with significant recoveries among tigers, manatees, grizzly bears, bluefin tuna and bald eagles.
"If we didn't make those efforts, the situation would have been much worse," Lambertini said.
But the onslaught of hunting, shrinking habitat, pollution, illegal trade and climate change—all caused by humans—has been too much to overcome, he acknowledged.
"Scientists call it the 'great acceleration'," he said in a phone interview.

"It is the exponential growth over the last 50 years in the use of energy, water, timber, fish, food, fertiliser, pesticides, minerals, plastics –- everything."
'New deal' for nature
The pace of population increase—long taboo in development and conservation circles—also took off around 1950, the date scientists have chosen as the "gold spike," or starting point, for a new geological period dubbed the Anthropocene, or "age of man".
In looking for answers, conservationists are turning to climate change for inspiration.
"We need a new global deal for nature," said Lambertini, noting two key ingredients in the 195-nation Paris climate treaty.
"One was the realisation that climate change was dangerous for the economy and society, not just polar bears," he said.
Similarly, he argued, threatened ecosystem services long taken for granted—drinkable water, breathable air, heat-absorbing oceans, forests that soak up CO2, productive soil—are worth tens of trillions of dollars every year.
"A healthy, sustainable future for all is only possible on a planet where nature thrives and forests, oceans and rivers are teeming with biodiversity and life," said Lambertini.
The Paris Agreement, negotiated under the UN convention on climate change, also set a clear target: global warming must be held to "well below" 2C, and 1.5C if possible.
The parallel UN Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), by contrast, has lots of targets running out to 2020 which are not only too weak, but—with one possible exception—will probably not be met, Lambertini said.
"The CBD is failing," he told AFP. But an upcoming meeting of the 195-nation body could be the beginning of a "revolution" that will see the Convention re-engineered in 2020 into "a new deal for Nature."
© 2018 AFP