Why did rainfall over Asian inland plateau region undergo abrupt decrease around 1999?
The Asian inland plateau (AIP) is located in the East Asian monsoon marginal areas and mainly includes Mongolia and part of northern China. Covering arid and semi-arid regions, the climate variability of the AIP is complex and can have profound impacts on economic and social activities.
Recently, scientists from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics worked with Korean and Russian scientists on the summer rainfall over the AIP region. They found an interdecadal change around 1998/99, with a rainfall decrease of about 16% of the climatological amount. Since rainfall plays a crucial role in drought conditions, this abrupt rainfall decrease significantly influenced the regional drought situation over the AIP. Time series of three drought indices all shift from positive to negative in 1999, indicating an exacerbation of the drought conditions.
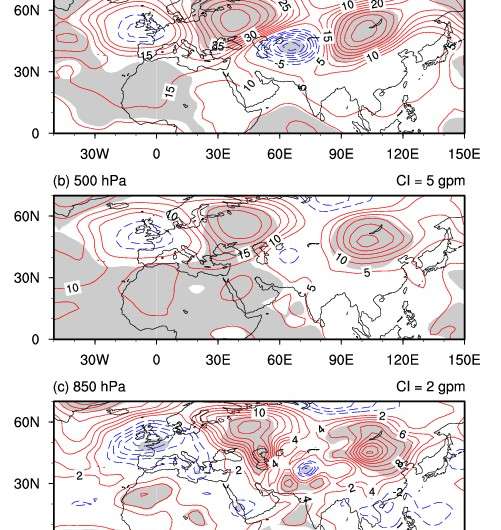
The driving factor for this interdecadal change is suggested to be a quasi-zonal wave-like pattern over the Eurasian continent. During 1999-2007, positive geopotential anomalies were located over Eastern Europe and the AIP, with negative anomalies over Western Europe and Central Asia. This teleconnection pattern, together with anticyclonic circulation over the AIP, was responsible for the decrease in summer AIP rainfall. The study further indicates that the warming SST anomalies over the North Atlantic could have excited the teleconnection pattern over the Eurasia, resulting in the rainfall decrease over the AIP and worsening the drought conditions there.
More information: Jinling Piao et al, An abrupt rainfall decrease over the Asian inland plateau region around 1999 and the possible underlying mechanism, Advances in Atmospheric Sciences (2017). DOI: 10.1007/s00376-016-6136-5
Provided by Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences