Asteroid zips by Orion nebula
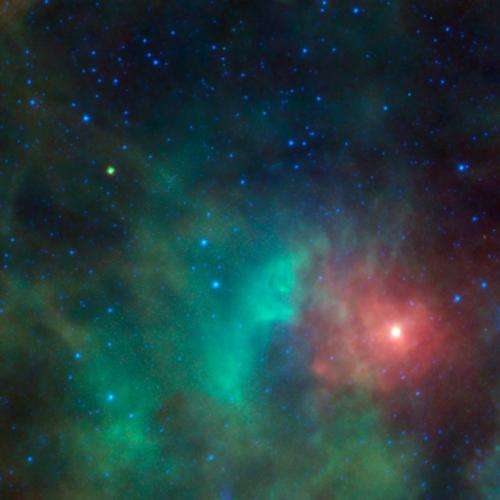

(Phys.org) —This image shows the potentially hazardous near-Earth object 1998 KN3 as it zips past a cloud of dense gas and dust near the Orion nebula. NEOWISE, the asteroid-hunting portion of the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, mission, snapped infrared pictures of the asteroid, seen as the yellow-green dot at upper left. Because asteroids are warmed by the sun to roughly room temperature, they glow brightly at the infrared wavelengths used by WISE.
Astronomers use infrared light from asteroids to measure their sizes, and when combined with visible-light observations, they can also measure the reflectivity of their surfaces. The WISE infrared data reveal that this asteroid is about .7 mile (1.1 kilometers) in diameter and reflects only about 7 percent of the visible light that falls on its surface, which means it is relatively dark.
In this image, blue denotes shorter infrared wavelengths, and red, longer. Hotter objects emit shorter-wavelength light, so they appear blue. The blue stars, for example, have temperatures of thousands of degrees. The coolest gas and dust appears red. The asteroid appears yellow in the image because it is about room temperature: cooler than the distant stars, but warmer than the dust.
Provided by NASA