September 17, 2012 weblog
Group develops carbon nanotube based flexible display using flexographic printing technology
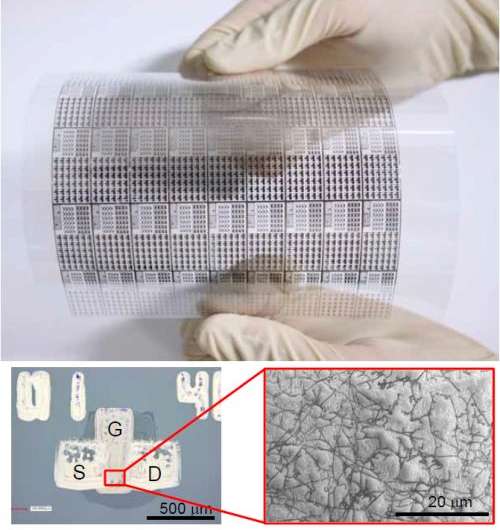
(Phys.org)—A group of researchers from Nagoya University and Bando Chemical Industries Ltd has partnered to create a flexible thin film transistor (TFT) display based on carbon nanotubes using flexographic printing technology. The team announced their results at the recent Japan Society of Applied Physics Autumn Meeting in Tokyo.
Flexographic printing is a type of printing that involves using a flexible relief (raised) ink coated plate to apply a wide range of ink types to a wide range of materials (substrates). Product is creating by rolling a substrate though a device allowing for patterns to be applied as it moves. Ink is applied to the plate via a roll and photo curing is used to create the final product. Flexographic printing has become a popular means for printing on a wide variety of materials such as cardboard and plastics and is lauded for its ability to cover wide areas of material with solid even coloring. In this new effort, the research team applied the underlying concepts of flexographic printing to the production of thin film transistor displays in hopes of producing such displays at a higher rate than is achievable by standard methods including ink-jet. They suggest that such a process could be easily implemented as well because of its compatibility with existing roll-to-roll methods.
The team said that besides increased throughput, using the flexographic technique allowed for the production of TFTs at room temperatures and normal air pressure which they say would lower costs in a production environment. The structure of the resulting TFT comes from the creation of flexible integrated circuits via application to a transparent substrate using a floating-catalyst chemical vapor deposition technique which is followed by gas-phase filtering and transfer. The end result is a carbon nanotube network that can be used as the basis for a flexible display for computers or hand-held electronic devices. The process also offers a means for creating the points of contact between the TFT and metal wiring that lead to other display components.
The team notes that while the precision of the flexographic technique is slightly lower than that for gravure printing, the pace is higher, allowing for a printing speed of 6.6cm per second.
More information:
via Tech-On
© 2012 Phys.org