Antarctic Demolition is Underway: Scientists witness hundreds of cracks in the sea ice

Car demolition derbies last minutes, but when it comes to a giant iceberg near Antarctica it takes a bit longer. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on board the Terra and Aqua satellites captured images of iceberg B-15A steaming a steady course towards the extended Drygalski Ice Tongue and scientists expected the Long Island, NY sized berg to initiate a colossal collision by January 15. Instead B15A appears to have grounded on a submarine shoal when it was just 2.5 miles from the glacier. Continued observations of the area on the eve of what is expected to be renewed iceberg movements have shown a sudden break up sea ice around the iceberg.
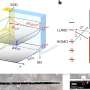
Image: The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites captured the above image January 17, 2005 and others recently.
These waters pass through an annual cycle in which thick ice freezes on the water during Antarctica's frigid winter, then breaks and drifts into the Ross Sea during the summer. By mid summer in January, much of this ice has typically been swept from the area. This year, the process was disrupted by the giant B-15A iceberg. Topping 129 kilometers (80 miles) in length, the Long Island-sized iceberg blocked the currents that usually clear out this ice. As late as the first week of January, the sea ice remained intact. The frozen expanse of water between the shore (left) and the open sea (right) had been a serious problem for penguins, which had to travel a greater distance to reach open waters and food. Though adults were probably able to make the trip to feed, scientists feared the adults would have to consume most of the food they were bringing to their chicks because of the increased length of the return journey. While the breaking ice may shorten the trip and bring relief to the penguins, it is not clear if the changing conditions will save penguin chicks from starvation. The ice was also a potential problem for supply ships trying to reach McMurdo Station and Scott Base. Instead of cutting through the usual 64 kilometers (40 miles) that separate the pier from open waters, icebreakers had to chart a course through 129 kilometers (80 miles) of ice. The icebreaker succeeded in reaching McMurdo in early January.
The image also reveals that the B-15A iceberg has drifted away from the Drygalski Ice Tongue. The massive iceberg had been on course to strike the ice tongue in what could have been a collision of giants. The Drygalski Ice Tongue is a floating extension of a land-based glacier. Such ice tongues have been known to break under smaller strains, and according to NASA scientist Robert Bindschadler, the Drygalski Ice Tongue has never experienced a blow of the magnitude that B-15A could deliver. The iceberg had been moving steadily towards the ice tongue, but its movement slowed in late December. Just as the gap between the two narrowed to less than 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) , the iceberg rotated slightly and may have become grounded. By January 13, the gap widened as the iceberg appeared to reverse its course, perhaps in response to being grounded, says Bindschadler
Source: NASA (by Rani Chohan and Holli Riebeek)