Last update:
Bio & Medicine news

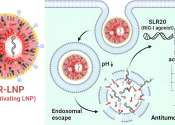
Unveiling cancer's hidden messengers: How extracellular vesicles aid tumor spread
Most cells in the body send out little messengers called extracellular vesicles that carry proteins, lipids, and other bioactive molecules to other cells, playing an important role in intercellular communication. But healthy ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 14, 2025
0
51

Biomolecular 'silly putty': High-res imaging of cellular condensates achieved using fluorogen technology
Biomolecular condensates are shifting blobs in our cells that organize cellular matter. They are distinct molecular communities made of DNA, RNA and proteins that "condense" molecules to key locations, yet they frequently ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 14, 2025
0
11

Implantable biosensors get major longevity boost with coating technology that inhibits biofouling
Wearable and implantable biosensors that can accurately detect biological molecules in a non- or minimally invasive manner have vast potential for monitoring patients' physiology and response to therapies. For example, wearable ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 13, 2025
0
0

Nanotube separation technique advances precise sensors for continuous health monitoring
Researchers at the University of Turku, Finland, have succeeded in producing sensors from single-wall carbon nanotubes that could enable major advances in health care, such as continuous health monitoring. Single-wall carbon ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 13, 2025
0
19

Electrocatalytic sterilization: Nanowires produce localized highly alkaline microenvironments to kill bacteria
Harmful microorganisms such as bacteria represent one of the largest threats to human health. Efficient sterilization methods are thus a necessity.
Bio & Medicine
Mar 13, 2025
0
25

New capabilities in DNA nanostructure self-assembly eliminate need for extreme heating and controlled cooling
University at Albany researchers at the RNA Institute are pioneering new methods for designing and assembling DNA nanostructures, enhancing their potential for real-world applications in medicine, materials science and data ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 12, 2025
0
74

Nanogel drug delivery system shows promise for treating recurrent urinary tract infections
Researchers from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus studied a new method to deliver antibiotics, specifically gentamicin, directly into the bladder tissue to better treat UTIs. They did this by creating nanogels ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 12, 2025
0
56

Lighting the way: How activated gold nanoparticles reveal drug movement in the body
Tracking targeted drug delivery is often a challenge due to limitations in current imaging techniques. A recent study by Tokyo's Waseda University reports a breakthrough imaging technique that allows direct and highly sensitive ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 12, 2025
0
0

'Nanosnag' virus detection technique could streamline vaccine production quality checks
As viral vaccines are increasingly used to meet global health needs, the pharmaceutical industry is manufacturing larger amounts of virus to make them. A new method of virus detection from researchers at Carnegie Mellon University's ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 12, 2025
0
0

Smartphone and nanotechnology enable rapid neonatal jaundice detection
A research team led by Prof. Jiang Changlong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed an innovative dual-mode sensing platform using upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs). ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 11, 2025
0
47

Zebrafish study reveals nanoplastics' impact on red blood cell maturation
Polystyrene nanoparticles are widely used in packaging, but their effects on organisms are unclear. Very little was known about how they affect blood cell development until now.
Bio & Medicine
Mar 11, 2025
0
0

Bio-based polyester nanocomposites offer high performance and reprocessability
A research team led by Prof. Zhu Jin from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has synthesized a novel bio-based polyester nanocomposite with high performance ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 11, 2025
0
0

Smart humidity sensor monitors human behavior through respiratory patterns
A cutting-edge humidity sensing system has been unveiled, capable of monitoring human behaviors in real-time through the detection of respiratory patterns. This breakthrough technology integrates a highly sensitive humidity ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 11, 2025
0
0

Liquid nanofoam innovation designed to protect the brain now tested on internal organs
Researchers at Michigan State University have refined an innovation that has the potential to improve safety, reduce severe injury and increase survival rates in situations ranging from car accidents, sports, law enforcement ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 11, 2025
0
36

Experiments aboard the International Space Station may offer promising advancements in fighting cancer
Getting seven experiments on the International Space Station requires a really good idea. Like a brand new way to attack tumors—one that you can only make in space.
Bio & Medicine
Mar 11, 2025
0
2

Sperm motility and droplet adhesion: A novel approach could make at-home male fertility tests a reality
A new way to measure male fertility has been discovered by researchers at the University of Waterloo, opening the door to the development of simple, inexpensive tests for clinical and at-home use.
Bio & Medicine
Mar 10, 2025
0
33

Carbon nanotubes and machine learning: A new way to spot subtle immune cell differences
Early diagnosis is crucial in disease prevention and treatment. Many diseases can be identified not just through physical signs and symptoms but also through changes at the cellular and molecular levels.
Bio & Medicine
Mar 10, 2025
0
7

Precision cancer treatment using magnet-guided, heat-activated nanoparticles
Traditionally, radiation, chemotherapy, and surgery have been the most common ways to remove and destroy malignant cells. However, because these treatments can also damage healthy cells, they often have significant side effects. ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 6, 2025
0
13

Nanoparticle immune therapy shows potential to halt pancreatic cancer spread
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the most challenging tumors to treat, partly because it is often discovered at advanced stages when the disease has already spread, or metastasized. About half of pancreatic cancer patients ...
Bio & Medicine
Mar 5, 2025
0
110

Innovations in core-shell nanoparticles advance drug delivery and precision medicine
A review in OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology explores how core-shell nanoparticles could revolutionize drug delivery systems and play a key role in advancing personalized and precision medicine.
Bio & Medicine
Mar 5, 2025
0
0
Other news

Why does nature love spirals? The link to entropy

Boosting the response speed of quantum LEDs via an excitation memory effect

Crew launch to ISS paves way for 'stranded' astronauts' return

Melanosome patterns in Mesozoic mammals suggest they had dark, uniformly dull fur coloring

Physicists use optical vortex beams to control atom ionization

Tapuy rice wine fermentation yields possible anti-aging superfood