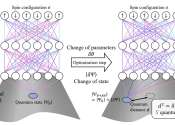
Floquet engineering tunes ultracold molecule interactions and produces two-axis twisting dynamics
The interactions between quantum spins underlie some of the universe's most interesting phenomena, such as superconductors and magnets. However, physicists have difficulty engineering controllable systems in the lab that ...