Probing Question: Why are babies cute?
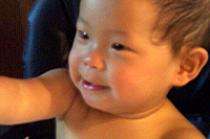
Babies hold an almost universal appeal, even for the grouchiest of people. There's just something about their big shining eyes and button noses that draws people in and stirs their most tender feelings.
In short, babies are cute.
This cuteness is so obvious that people take it for granted. But what exactly is it about a baby that prompts those "oohs" and "ahs"?
Image: Resistance is futile. Photo by Lori Pacchioli
"We are inherently attracted to a specific set of characteristics, including large, symmetrical heads, large eyes, small mouths and small noses," according to Jeffrey Kurland, associate professor of biological anthropology and human development. But why do almost all humans find this particular set of features so appealing?
Kurland said the answer lies in evolution. According to Darwin, individuals of a given species will exhibit a new trait if that trait provides a survival advantage, boosting an organism's chances of living to see sexual maturity and successfully reproduce. But what does evolutionary fitness have to do with being cute?
One of two basic processes may be at work, Kurland suggested. In the first, a distant female ancestor was born with a slightly different makeup than her forebears, perhaps the result of some random genetic mutation. This change in her genes caused her to prefer babies with the features we see as cute. She passed on this preference to future generations, and thereafter infants with "cuteness" attracted more attention and received more care than their less-cute compatriots. The cuties therefore were more likely to survive and reproduce, and their offspring inherited both their "cuteness" trait and their preference for cuteness. "Because the two traits became linked in this way, they both increased in the population," said Kurland.
The second evolutionary possibility is much like the first, except that here cuteness runs more than skin deep. In this scenario, too, Kurland explained, a fore-mother was born with an arbitrary preference for "cute" babies -- to her they just look better. And again, she gives more attention and care to her "cute" babies, who survive in greater numbers to pass on both their own cuteness genes and the genes for her preference, and this genetic combination gradually increases in the population.
In this case, however, the babies do not merely look better -- they are better, from an evolutionary standpoint. According to Kurland, infants who displayed cute features actually may have been healthier, and as adults more sexually attractive. They would have been more likely to survive and reproduce. Cuteness, in this case, is an indicator of good genes.
Again, the mother's preference trait and the infant's cuteness trait reinforce each other. Over many generations, mothers keep selecting cuter, and in turn strengthening their preferences.
In both cases, Kurland stressed, cuteness and the preference for cuteness are passed on not just through female offspring, but through males as well. Fathers, uncles and big brothers -- as well as aunts and grandmas and family friends -- will prefer infants who are as cute as they themselves were. "The two traits spread through the entire population."
At some point in the distant past, it would seem, babies were not all cute. Their particular physical characteristics attracted no special attention. But once the "cuteness" preference took hold in the genes, babies had no choice but to become cuter over the generations. In effect, they had to wage a kind of cuteness war to get attention -- and to this day people seemingly are helpless against the onslaught.
Source: By Tom Fitzgerald, Research/Penn State

















