TOI-837 b is a young Saturn-sized exoplanet with a massive core, observations find
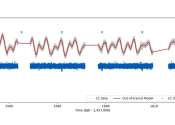
European astronomers have performed photometric and spectroscopic observations of a distant giant exoplanet known as TOI-837 b. As a result, they found that TOI-837 b is a young Saturn-sized planet containing a massive core, ...