New research sheds light on relationships between plants and insects in forest ecosystems
U.S. Forest Service researchers and partners published new findings on how leaf-eating insects affect forest ecosystems worldwide.

U.S. Forest Service researchers and partners published new findings on how leaf-eating insects affect forest ecosystems worldwide.
Ecology
Aug 3, 2024
0
42

Krill in northern waters show how key marine species can adapt genetically to cope with climate change. This discovery was made by researchers at Uppsala University in collaboration with an international research group. According ...
Evolution
Aug 1, 2024
0
2
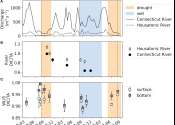
New York's Long Island Sound (LIS) is an important inlet and estuary in the North Atlantic Ocean, which is highly urbanized due to its proximity to the city. This daily activity of passenger transport, fishing and cargo ships ...

A research team has demonstrated that using plant factory technology (PFT) to precisely control environmental factors can significantly enhance vegetable quality. By cultivating a new lettuce cultivar in a PFT system, they ...
Biotechnology
Jul 29, 2024
0
1

A University of Kentucky study titled "Productivity benefits of cereal-legume cover crop mixtures under variable soil nitrogen and termination times" suggests that mixing cover crops is a beneficial strategy for modern agriculture.
Agriculture
Jul 17, 2024
0
0

A research team has identified three rhizobia strains, Rhizobium sp. TZSR12C, Rhizobium sp. TZSR25B, and Bradyrhizobium sp. TZSR41A, which effectively suppressed root rot fungal pathogens in soybeans under both in vitro and ...
Biotechnology
Jul 17, 2024
0
1

Carotenoids, vital antioxidants in plants, are integral for human health, enhancing immunity and preventing diseases. However, many vegetables, including Chinese kale, naturally exhibit low carotenoid levels.
Molecular & Computational biology
Jul 9, 2024
0
0

A string of whale strandings on the East Australian Coastline and questions around the appropriate disposal methods for the remains has prompted a new study that highlights sustainable, cultural and ecosystem beneficial offshore ...
Ecology
Jul 9, 2024
0
0

Soil stores large amounts of organic carbon, whose dynamic changes can cause a huge impact on the global climate system. Forest succession is a long-term ecological process that can exert powerful effects on soil organic ...
Ecology
Jul 8, 2024
0
57

Iron is a vital micronutrient for plants, essential for photosynthesis, respiration, and various metabolic processes. Despite its abundance in the soil, iron often exists in insoluble forms, particularly in calcareous soils, ...
Molecular & Computational biology
Jul 2, 2024
0
0
A nutrient is a chemical that an organism needs to live and grow or a substance used in an organism's metabolism which must be taken in from its environment. They are used to build and repair tissues, regulate body processes and are converted to and used as energy. Methods for nutrient intake vary, with animals and protists consuming foods that are digested by an internal digestive system, but most plants ingest nutrients directly from the soil through their roots or from the atmosphere.
Organic nutrients include carbohydrates, fats, proteins (or their building blocks, amino acids), and vitamins. Inorganic chemical compounds such as dietary minerals, water, and oxygen may also be considered nutrients. A nutrient is said to be "essential" if it must be obtained from an external source, either because the organism cannot synthesize it or produces insufficient quantities. Nutrients needed in very small amounts are micronutrients and those that are needed in larger quantities are called macronutrients. The effects of nutrients are dose-dependent and shortages are called deficiencies.
See healthy diet for more information on the role of nutrients in human nutrition.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA