Charge your laptop in a minute? Supercapacitors can help; new research offers clues
Imagine if your dead laptop or phone could charge in a minute or if an electric car could be fully powered in 10 minutes.

Imagine if your dead laptop or phone could charge in a minute or if an electric car could be fully powered in 10 minutes.
Condensed Matter
May 25, 2024
1
227

Many of today's quantum devices rely on collections of qubits, also called spins. These quantum bits have only two energy levels, the "0" and the "1." However, spins in real devices also interact with light and vibrations ...
Condensed Matter
May 24, 2024
0
87
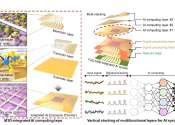
Electrostatic capacitors play a crucial role in modern electronics. They enable ultrafast charging and discharging, providing energy storage and power for devices ranging from smartphones, laptops and routers to medical devices, ...
Nanomaterials
Apr 18, 2024
0
49

Electron spin states can now be probed at much higher resolution and more efficiently, opening new opportunities in materials analysis and data processing technologies.
Condensed Matter
Apr 17, 2024
0
36

Dual topological phases have been discovered in an intrinsic monolayer crystal, a finding that reveals new and unique rule-bending properties in a quantum material, an international team of scientists led by Boston College ...
Condensed Matter
Apr 2, 2024
0
10

From pacemakers to neurostimulators, implantable medical devices rely on batteries to keep the heart on beat and to dampen pain. But batteries eventually run low and require invasive surgeries to replace.
Materials Science
Mar 27, 2024
1
164

Dirac electrons were predicted by P. Dirac and discovered by A. Geim, both of whom were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 and in 2010, respectively. Dirac electrons behave like photons rather than electrons, for ...
Condensed Matter
Mar 14, 2024
0
2513

Every over-the-counter medication bottle sports a protective seal, usually a plastic wrap or foam layer, or both. These seals offer signs of tampering attempts. In a parallel concern, the International Atomic Energy Agency ...
Analytical Chemistry
Feb 13, 2024
0
3

Superhydrophobic surfaces, characterized by their ability to repel water with a contact angle above 150° and a sliding angle below 10°, offer a range of applications from self-cleaning and anti-corrosion to oil/water separation ...
Analytical Chemistry
Feb 8, 2024
0
0

Our phones and electronic devices could soon be smaller and sleeker without the risk of overheating thanks to microcapsules that transform in the blink of an eye.
Materials Science
Jan 16, 2024
0
24