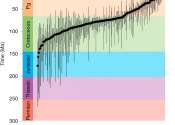
Discovery of new ancient giant snake in India
A new ancient species of snake dubbed Vasuki Indicus, which lived around 47 million years ago in the state of Gujarat in India, may have been one of the largest snakes to have ever lived, suggests new research published in ...