Scientists unravel 'Hall effect' mystery in search for next generation memory storage devices
An advance in the use of antiferromagnetic materials in memory storage devices has been made by an international team of physicists.

An advance in the use of antiferromagnetic materials in memory storage devices has been made by an international team of physicists.
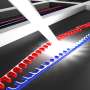
Using a network of vibrating nano-strings controlled with light, researchers from AMOLF have made sound waves move in a specific irreversible direction and attenuated or amplified the waves in a controlled manner for the ...
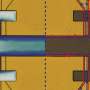
A hallmark of so-called topological quantum states is that they are protected against local perturbations. ETH physicists now demonstrate that in the paradigmatic case of the integer quantum Hall effect, vacuum fluctuations ...

The kagome pattern, a network of corner-sharing triangles, is well known amongst traditional Japanese basket weavers—and condensed matter physicists. The unusual geometry of metal atoms in the kagome lattice and resulting ...
The world we experience is governed by classical physics. How we move, where we are, and how fast we're going are all determined by the classical assumption that we can only exist in one place at any one moment in time.
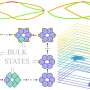
When can we say that a certain property of a system is robust? Intuitively, robustness implies that, even under the effect of external perturbations on the system, no matter how strong or random, said property remains unchanged. ...

An international team led by researchers at Princeton University has uncovered a new pattern of ordering of electric charge in a novel superconducting material.

The electronic structure of metallic materials determines the behavior of electron transport. Magnetic Weyl semimetals have a unique topological electronic structure—the electron's motion is dynamically linked to its spin. ...

Identical twins might seem 'indistinguishable,' but in the quantum world the word takes on a new level of meaning. While identical twins share many traits, the universe treats two indistinguishable quantum particles as intrinsically ...
Electric current is deflected by a magnetic field—in conducting materials, this leads to the so-called Hall effect. This effect is often used to measure magnetic fields. A surprising discovery has now been made at TU Wien, ...