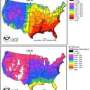
Study helps narrow down one reason why clouds are hard to model
Airborne particles known as "aerosols" strongly impact the way clouds form and change, but accurately capturing this effect in computer climate models has proved to be notoriously difficult. A new study in the Proceedings ...