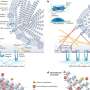
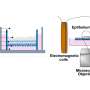
The analgesic effects of cooling or menthol are disrupted by inflammation, but scientists have not been clear how inflammation interferes with cold perception, until now. Credit: Dept. Pharmacology, University of Cambridge.
(Medical Xpress) -- Research groups at the University of Cambridge and the Instituto de Neurociencias, in Spain, have discovered a new and unexpected mechanism by which cold sensation is regulated, and opens up the possibility of developing drugs to mimic the well-known analgesic effects of cold and menthol.
The sensation of coolness is essential for our everyday life. Although extreme cold causes pain, moderate cooling inhibits pain, such as holding a burned hand under a cold tap. Another way to produce a sensation of coolness, and therefore to relieve pain, is to apply menthol, a compound present naturally in mint and widely used in peppermints, mentholated cigarettes and in pain-relieving rubs.
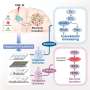
Cooling works by activating a protein named TRPM8, an ion channel which allows electric charge to flow across cell membranes. Menthol produces a sensation of coolness by acting on the same protein.
Unfortunately, the analgesic effects of cooling or menthol are disrupted by inflammation, but to date scientists have not been clear how inflammation interferes with cold perception.
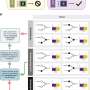
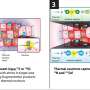
Dr. Xuming Zhang and Professor Peter McNaughton at the Department of Pharmacology, University of Cambridge, have found that a novel mechanism is responsible – a critical intermediate protein, called a Gq protein, binds directly to TRPM8 and when compounds, such as histamine, are released by inflammation, Gq is rapidly activated and switches TRPM8 off. Cold sensation is therefore deactivated by inflammation. The findings suggest that reversing this process, and reactivating cold sensation, may be a useful analgesic strategy.
“This novel mechanism opens up the possibility that the cold pathway could be manipulated clinically simply by disrupting the interaction of Gq protein with the TRPM8 channel” Dr. Zhang said.
The finding that Gq directly inhibits TRPM8 is surprising because while Gq is involved in several cellular signalling process, it has not previously been thought to act on ion channels in this way.
The research is published today in the journal Nature Cell Biology.
Journal information: Nature Cell Biology
Provided by University of Cambridge