Essential protein for the formation of new blood vessels identified
New research explains how cells regulate their bonds during the development of new blood vessels. For the first time, the role of the protein Raf-1 in determining the strength of the bond between cells has been shown. If Raf-1 is not present, the cells cannot stick together and the formation of new blood vessels is inhibited. This discovery may one day lead to new approaches to cancer treatment.
Angiogenic sprouting, the process by which new blood vessels grow from existing vessels, is a double-edged sword. It enables the cardiovascular system to develop in the embryo, and is vital for tissue regeneration in adults. But it also supplies growing tumors with nutrients and oxygen.
Angiogenesis is an example of collective cellular migration. Cells move as a group, held together by connections called adherens junctions. For the cells to move, they have to make and break these connections continuously. If the junctions are too stiff, they will not be able to move at all, but if they are too weak, the groups of cells will break apart. How this mechanism is controlled was unknown.
The mechanism has now been uncovered by Manuela Baccarini’s group at the Max F. Perutz Laboratories, a joint venture of the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna, who investigate cell signaling. They have established a crucial role for Raf-1, a multi-purpose signal transducer, in this process.
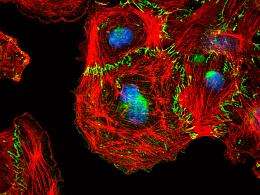
“The real breakthrough came when we were able to use video microscopy on the developing vessels in vitro,” explains the paper’s first author Reiner Wimmer. “We realized that the cells without Raf-1 were actively migrating, but only as single cells. They could not migrate in a group.”
The meaning of this discovery became clear in further experiments: the role of Raf-1 is to bring the new adherens junctions a kinase they need for the remodeling of the cytoskeleton. This means that Raf-1 is fine-tuning the bonds between the migrating cells by causing the local remodeling of the cell’s cytoskeleton.
As the process of angiogenic sprouting is necessary for the growth of tumors, this new discovery may one day be applied to produce cancer therapies to target Raf-1 and the other parts of this control mechanism, thereby disrupting the environment of the tumor.
More information: Wimmer R, et al. (2011). Angiogenic sprouting requires the fine-tuning of endothelial cell cohesion by the Raf-1/Rok-α complex. Developmental Cell. DOI:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.11.012 , PMID: 22209329