Japan moon probe survives second lunar night
Japan's moon lander woke up after unexpectedly surviving a second frigid, two-week lunar night and transmitted new images back to Earth, the country's space agency said Thursday.

Japan's moon lander woke up after unexpectedly surviving a second frigid, two-week lunar night and transmitted new images back to Earth, the country's space agency said Thursday.
Space Exploration
Mar 28, 2024
0
311
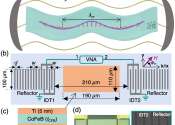
A team led by researchers from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science in Japan has succeeded in creating a strong coupling between two forms of waves—magnons and phonons—in a thin film. Importantly, they achieved ...
Condensed Matter
Mar 29, 2024
0
542

Physicists have observed a novel quantum effect termed "hybrid topology" in a crystalline material. This finding opens up a new range of possibilities for the development of efficient materials and technologies for next-generation ...
Condensed Matter
Apr 10, 2024
0
964

How fast can a neutron star drive powerful jets into space? The answer, it turns out, is about one-third the speed of light, as our team has just revealed in a new study published in Nature.
Astronomy
Mar 30, 2024
0
296

Hail is a semi-frequent visitor to winter, and occasionally summer, seasons across the globe and tends to pass by in a short but sharp downpour that can often be overlooked. However, sometimes these meteorological phenomena ...

New findings have revealed a coastal realm highly sensitive to changes in runoff and rainfall on land.
Earth Sciences
Apr 3, 2024
0
161

Billions of years ago, Mars was home to abundant water, and its Gale crater contained a lake. Gradually, the climate changed, drying the red planet and creating the dusty desert world we know today.
Planetary Sciences
Mar 22, 2024
1
1342

From abstract-looking cloud formations to roars of snow machines on ski slopes, the transformation of liquid water into solid ice touches many facets of life. Water's freezing point is generally accepted to be 32 degrees ...
Analytical Chemistry
Mar 20, 2024
0
112

Ever since its discovery in 2004, graphene has been revolutionizing the field of materials science and beyond. Graphene comprises two-dimensional sheets of carbon atoms, bonded into a thin hexagonal shape with a thickness ...
Nanomaterials
Apr 8, 2024
0
61

Three companies are in the running to provide NASA's next moon rover for crewed missions planned later this decade, the space agency said Wednesday.
Space Exploration
Apr 4, 2024
0
111
In mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball or bagel. On the other hand, there are surfaces which cannot be embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space without introducing singularities or intersecting itself — these are the unorientable surfaces.
To say that a surface is "two-dimensional" means that, about each point, there is a coordinate patch on which a two-dimensional coordinate system is defined. For example, the surface of the Earth is (ideally) a two-dimensional sphere, and latitude and longitude provide coordinates on it — except at the International Date Line and the poles, where longitude is undefined. This example illustrates that not all surfaces admits a single coordinate patch. In general, multiple coordinate patches are needed to cover a surface.
Surfaces find application in physics, engineering, computer graphics, and many other disciplines, primarily when they represent the surfaces of physical objects. For example, in analyzing the aerodynamic properties of an airplane, the central consideration is the flow of air along its surface.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA