Long-term forest study shows tornado's effects linger 25 years later
A long-term study at the University of Cincinnati has documented the rise of invasive species in a forest devastated by a tornado 25 years ago.

A long-term study at the University of Cincinnati has documented the rise of invasive species in a forest devastated by a tornado 25 years ago.
Ecology
Apr 10, 2024
0
33

Whether sipping nectar from flowers and zipping through the air, hummingbirds are a sure sign of spring in California.
Plants & Animals
Apr 4, 2024
0
17

Artificial Intelligence can be used to detect invasive Asian hornets and raise the alarm, new research shows. University of Exeter researchers have developed VespAI, an automated system that attracts hornets to a monitoring ...
Ecology
Apr 3, 2024
0
68

Every weekend, thousands of citizen scientists head into the great outdoors. If they see an unusual animal, plant or fungi, they take a photo and upload it.
Ecology
Apr 2, 2024
0
6

On a recent weekday, short but mighty flames began consuming an expanse of tallgrass in Illinois' Nachusa Grasslands, their advance marked with crackles and pops.
Ecology
Apr 1, 2024
0
15
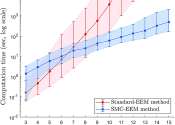
A new way to analyze the effects of conservation actions on complex ecosystems has cut the modeling time from 108 days to six hours, QUT statisticians have found.
Ecology
Mar 27, 2024
0
56

Ants transported by humans out of their native zones reshape ant communities worldwide. A recent study in Nature Communications by the Department of Ecology and Evolution at the University of Lausanne (UNIL) shows that our ...
Plants & Animals
Mar 20, 2024
0
77

As the climate warms, the number of alien species on every continent is expected to increase 36% by 2050. Some alien species—that is, plants or animals that live outside their natural range—are invasive and can harm ecosystems ...
Ecology
Mar 13, 2024
0
20

Statistics made available in January 2024 show that while deforestation in the Amazon fell by half in 2023, it increased by 43% in the Cerrado, the Brazilian savanna. A research group at the State University of Campinas's ...
Ecology
Mar 12, 2024
0
29

During a walk through the Huntington Botanical Gardens with her mother one morning, Brenda Ramirez was alarmed by the sudden squawks, warbles, and screeches of troops of parrots flying overhead at great speed in tight, precise ...
Ecology
Mar 8, 2024
0
34
In biogeography, a species is defined as indigenous or native to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only natural resources, with no human intervention. Every natural organism (as opposed to a domesticated organism) has its own natural range of distribution in which it is regarded as native. Outside this native range, a species may be introduced by human activity; it is then referred to as an introduced species within the regions where it was anthropogenically introduced.
An indigenous species is not necessarily endemic. In biology and ecology, endemic means exclusively native to the biota of a specific place. An indigenous species may occur in more than one locale.
The terms endemic and indigenous do not imply that an organism necessarily originated or evolved where it is found.
This text uses material from Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY-SA