Researchers detect a new molecule in space
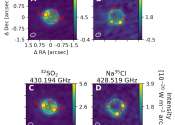
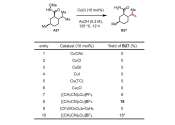
New research from the group of MIT Professor Brett McGuire has revealed the presence of a previously unknown molecule in space. The team's open-access paper, "Rotational Spectrum and First Interstellar Detection of 2-Methoxyethanol ...