Greenland (Danish: Grønland; Kalaallisut: Kalaallit Nunaat, meaning "Land of the people" ) is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically associated with Europe (specifically Denmark) since the 18th century.
In 1979, Denmark granted home rule to Greenland, with a relationship known in Danish as Rigsfællesskabet, and in 2008 Greenland voted to transfer more competencies to the local government. This became effective the following year, with the Danish royal government remaining in charge only of foreign affairs, security and financial policy, and providing a subsidy of Dkr3.4 billion ($633m), or approximately US$11,300 per Greenlander, annually.
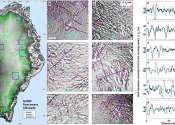
Greenland is, by area, the world's largest island that is not a continent in its own right, as well as the least densely populated country in the world. However, since the 1950s, scientists have hypothesized that the ice cap covering the country may actually conceal three separate island land masses that have been bridged by glacier.