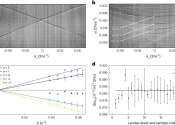
A shade closer to more efficient organic photovoltaics
Transparent solar cells will transform the look of infrastructure by enabling many more surfaces to become solar panels. Now, materials called non-fullerene acceptors that can intrinsically generate charges when exposed to ...