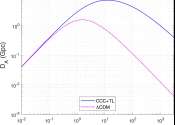
Model describes universe with no big bang, no beginning, and no end
(PhysOrg.com) -- By suggesting that mass, time, and length can be converted into one another as the universe evolves, Wun-Yi Shu has proposed a new class of cosmological models that may fit observations of the universe better ...