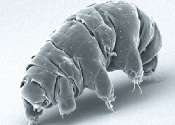
Tardigrades survive impacts of up to 825 meters per second
A pair of researchers at the University of Kent has found that tardigrades are able to survive impacts at speeds of up to 825 meters per second. In their paper published in the journal Astrobiology, Alejandra Traspas and ...