This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Porous crystals made from plant extracts purify water from pharmaceutical pollutants
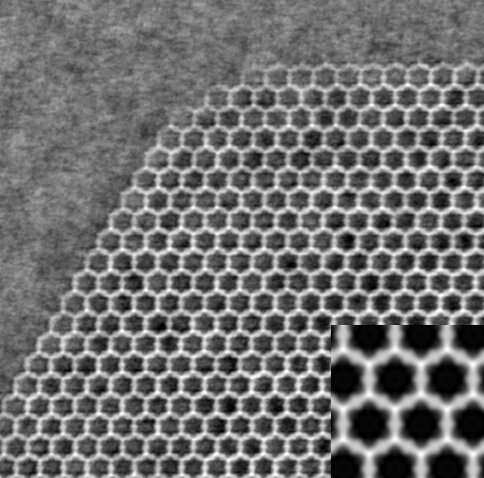
Researchers from Stockholm University have developed porous crystals made from pomegranate extract to capture and degrade pharmaceutical molecules found in local municipal wastewater. The research is published in the scientific journal Nature Water.
Pharmaceutical compounds affect the human body to improve our health, but they can also have unintentional adverse effects for the well-being of wildlife. Hence wastewater treatment plants are facing the challenge of removing emerging organic contaminants (EOCs) such as active pharmaceutical ingredients, and therefore new materials and technologies are required.
One strategy for removing pollutants from water is by using porous materials that behave like sponges. Metal-organic frameworks, so called MOFs, are a type of nanoporous material that are made of metal ions and organic molecules. Most MOFs are made using synthetic organic molecules. But now researchers from the Department of Materials and Environmental Chemistry, Stockholm University, have managed to develop new porous MOFs using a naturally occurring molecule found in plants—ellagic acid.
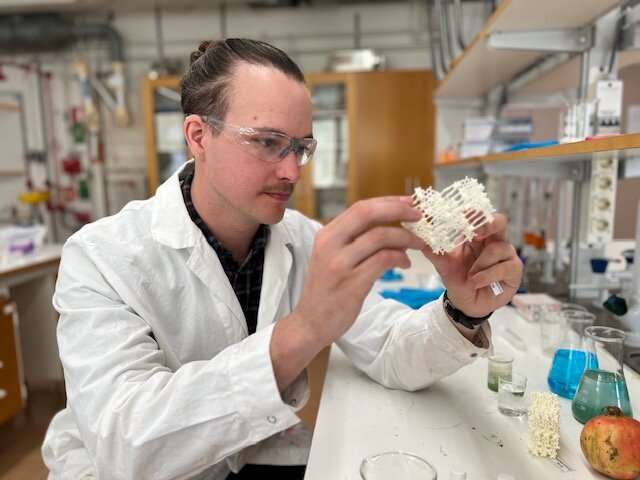
"Ellagic acid is one of the main building units of naturally occurring polyphenols known as tannins, which are common in fruits, berries, nuts, and tree bark. By combining ellagic acid, which was extracted from either pomegranate peel or tree bark, with zirconium ions, we developed a new highly porous MOF which we named SU-102," says Erik Svensson Grape, Ph.D. student at the Department of Materials and Environmental Chemistry.

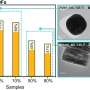
In order to test the performance of SU-102, water that had already been purified at a local wastewater treatment facility was further treated with the new MOF. The results showed that SU-102 removed many of the pharmaceutical pollutants that were not fully removed by the wastewater treatment facility. In addition to capturing the pharmaceutical pollutants, SU-102 was also used to break down pollutants using light in a process known as photodegradation.
"This has been a very exciting project as we got the opportunity to work directly with water samples from the treatment plant, thereby finding an application where our material could be put to use towards a very pressing environmental issue. We hope one day that SU-102 will be used on a bigger scale and also for other environmental applications," says Erik Svensson Grape at Stockholm University.
More information: Tom Willhammar, Removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from effluent by a plant-based metal–organic framework, Nature Water (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s44221-023-00070-z. www.nature.com/articles/s44221-023-00070-z
Journal information: Nature Water
Provided by Stockholm University