This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Study reveals influencing factors on global dumpsite distribution
With the advancement of global civilization, monitoring and managing dumpsites have become essential parts of environmental governance worldwide. However, dumpsite locations are difficult to pinpoint in a timely manner by local government agencies and environmental groups.
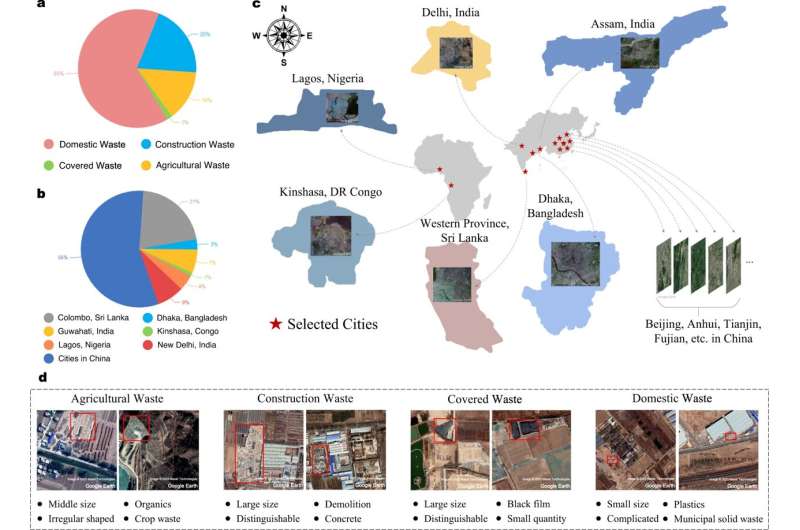
A study published in Nature Communications describes an efficient and intelligent dumpsite detection technique and analyzes the correlation between the number of dumpsites and social/economic factors.
The study was conducted by a research team from the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
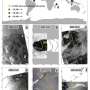
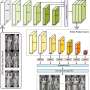
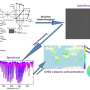
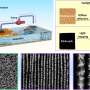
The team constructed the first fine-grained remote-sensing dumpsite dataset with optical satellite images and proposed a highly automated method for dumpsite detection combined with deep learning methods. The proposed approach reduces the investigation time by more than 96.8% compared with the manual method.
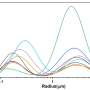
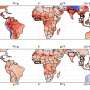
The researchers focused on the global distribution of dumpsites in urban areas. By analyzing the statistical correlation between the number of dumpsites and 18 social/economic factors in 28 cities worldwide, they found that the number of dumpsites was statistically correlated with factors such as development, urbanization and sanitation level but not with population density and education level.
More information: Xian Sun et al, Revealing influencing factors on global waste distribution via deep-learning based dumpsite detection from satellite imagery, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37136-1
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences