This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Protein domain common to plants and animals plays role in COVID-19 infection
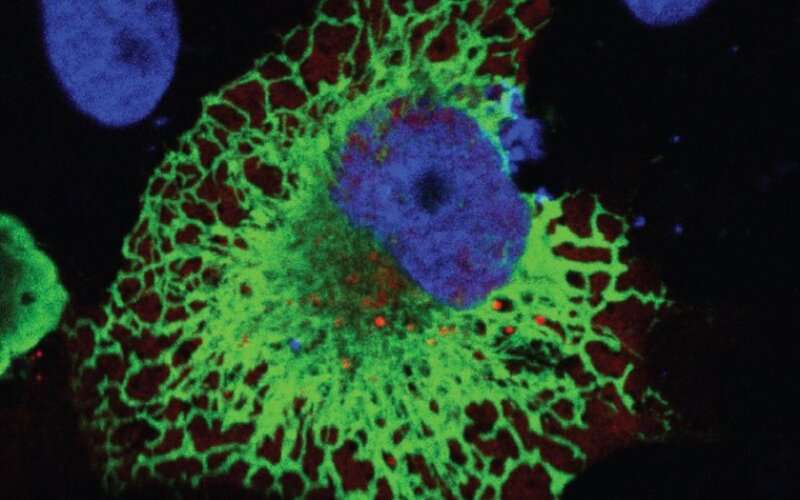
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists exploring bioenergy plant genetics have made a surprising discovery: a protein domain that could lead to new COVID-19 treatments.
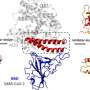
Researchers found the same plasminogen-apple-nematode, or PAN, domain studied by ORNL in plants like poplar and willow is also present in the human NRP1 receptor protein. NRP1 is less studied than the ACE-2 receptor targeted by current COVID-19 treatments, but this research shows its promise as a future therapeutic target.
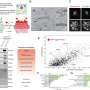
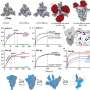
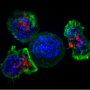
By mutating amino acids called cysteine residues in the PAN domain of NRP1, researchers disrupted the ability of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to use its spike protein to invade cells, as described in iScience. ORNL scientists have also linked PAN to the growth of cancerous tumors.
"This project provides more evidence that PAN is involved in host cell invasion," said ORNL's Wellington Muchero. "By pinpointing these amino acids, researchers could reduce viral interaction with host cells."
More information: Debjani Pal et al, Mutating novel interaction sites in NRP1 reduces SARS-CoV-2 spike protein internalization, iScience (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106274
Journal information: iScience
Provided by Oak Ridge National Laboratory