This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
Portable electrochemical sensor designed for lead ion detection
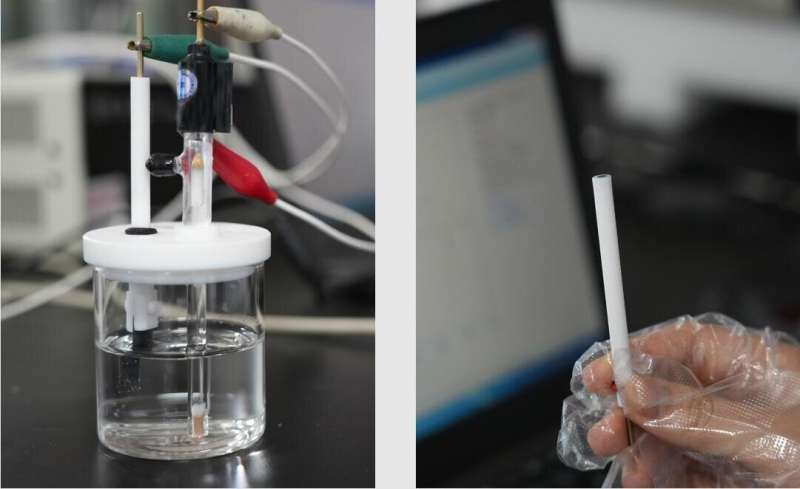

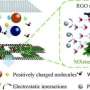
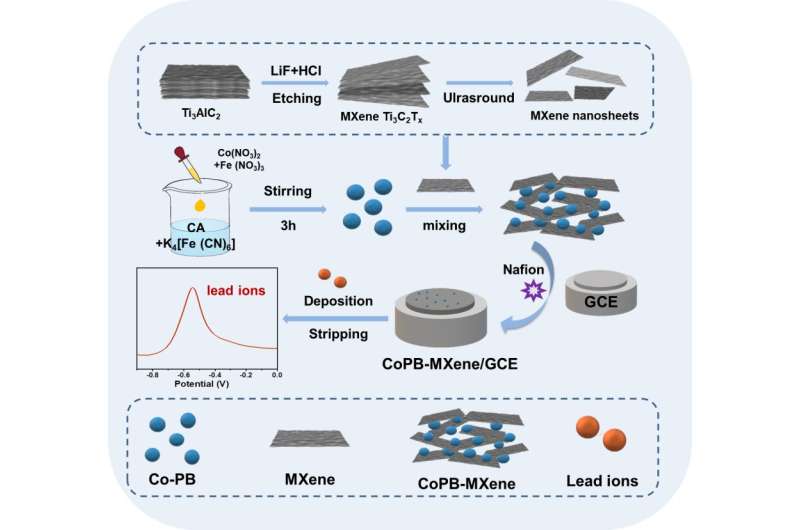
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Wu Zhengyan and Zhang Jia from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a portable electrochemical lead ion (Pb2+) sensor based on cobalt-doped Prussian blue (CoPB) combining MXene material, which possesses an enormous potential for Pb2+ detection in practical applications.
The results were published in Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry.
As a representative heavy metal ion pollutant, Pb2+ seriously affects the ecological environment and human health even at low concentration due to its high toxicity and easy accumulation in plants and animals. A direct and real-time detection for trace levels of Pb2+ appear to be particularly important in environmental waters.
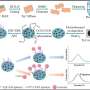
In this research, the team presented the development of a portable electrochemical sensor for detecting lead ions using CoPB combined with MXene.
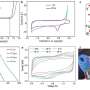
The composites of CoPB-MXene exhibited superior conductivity and stability, enabling a linear detection range of 1-200 nM at low deposition potential, with an ultra-low detection limit of 0.97 nM.
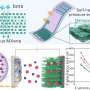
After investigating the influence of various operating conditions, including deposition time, buffer solution, and pH value, on the sensor performance, researchers determined optimal conditions, which helped CoPB-MXene/GCE exhibit excellent repeatability, high anti-interference, and remarkable reproducibility.
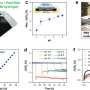
What impressed them most was that the sensor's response current remained at 89.23% of the initial value after four weeks.
Notably, CoPB-MXene/GCE demonstrated high accuracy in the detection of lead ions in different water samples, such as bottled water, tap water, groundwater, and lake water.
These results could pave the way towards the application of CoPB-MXene/GCE sensor in detecting lead ions.
More information: Xinyue Guo et al, Facile fabrication of 2D MXene loading Co-doped Prussian blue nanoparticles for ultrasensitive electrochemical assay of trace lead ions, Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2023.117320
Provided by Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences