This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Peering into ocular waste recycling
A recent study in the Journal of Biological Chemistry revealed the key to a protein that commonly causes blindness. The biological process involves a protein that is essential for transporting toxic compounds out of the eye, similar to a garbage recycling service. The challenge is that, like food and the waste it generates, these compounds are essential for the eye to function properly—until they build up and cause blindness.
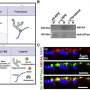
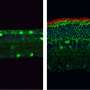
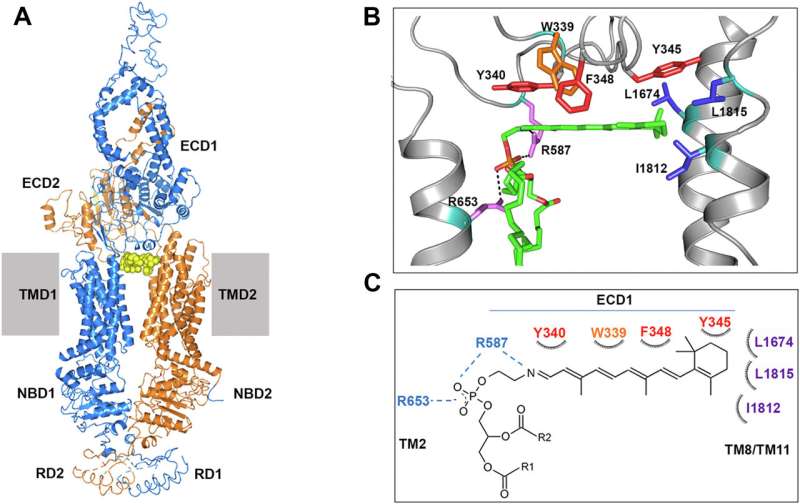
The scientists behind the study research a protein transporter, called ABCA4, that lines the edges of specialized photoreceptor cells in the retina and is normally poised to remove toxic, fatty retinal byproducts called N-Ret-PE. Retinal is a derivative of vitamin A, which is found in foods such as leafy green vegetables.
"Retinal is critical for vision," said Robert Molday, a professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at the University of British Columbia who oversaw the work. "But, it's also potentially very toxic because it has a very reactive element. So, cells have to be able to balance between using retinal for sustained vision as well as managing its toxicity."
Mutations in ABCA4 can cause N-Ret-PE buildup, which leads to vision loss in diseases such as Stargardt disease. Stargardt disease is the most common inherited form of macular degeneration and affects approximately 30,000 people nationwide. There is currently no therapy or cure for the disease.
The researchers were interested in finding out how the ABCA4 transporter malfunctions to cause vision loss. They found that a portion of the protein that interacts with N-Ret-PE, known as the binding pocket, is inert in some patients with Stargardt disease. Therefore, the toxic compounds slip out of the ABCA4 transporter and cannot be removed from the retina.
Next, by changing the makeup of ABCA4, the researchers showed they could mimic the effect of the Stargardt mutations.
"We were able to elucidate the mechanism of binding, which paves the way for treatments for Stargardt disease," Tongzhou Xu, a postdoctoral fellow at UBC and lead author of the study, said.
The team is optimistic that one day there will be a targeted therapeutic for patients with Stargardt disease that may use gene therapy and specialized particles for delivery to the eye. Gene therapy approaches have already been successfully used to correct mutations in a similar transporter, which causes cystic fibrosis.
"We are now applying two types of technologies to alter ABCA4," Molday said. "One which was developed to specifically correct the DNA with gene-editing approaches. We are coupling that with lipid nanoparticles, which have been used in the COVID-19 vaccine to encapsulate mRNA. So, by combining these two technologies, we envision being able to potentially correct the defects in individuals with Stargardt's disease that have specific point mutations."
More information: Tongzhou Xu et al, Retinal-phospholipid Schiff-base conjugates and their interaction with ABCA4, the ABC transporter associated with Stargardt Disease, Journal of Biological Chemistry (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104614
Journal information: Journal of Biological Chemistry