This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
proofread
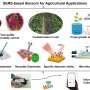
High-throughput sensor developed for detecting biochemical molecules with high sensitivity and specificity
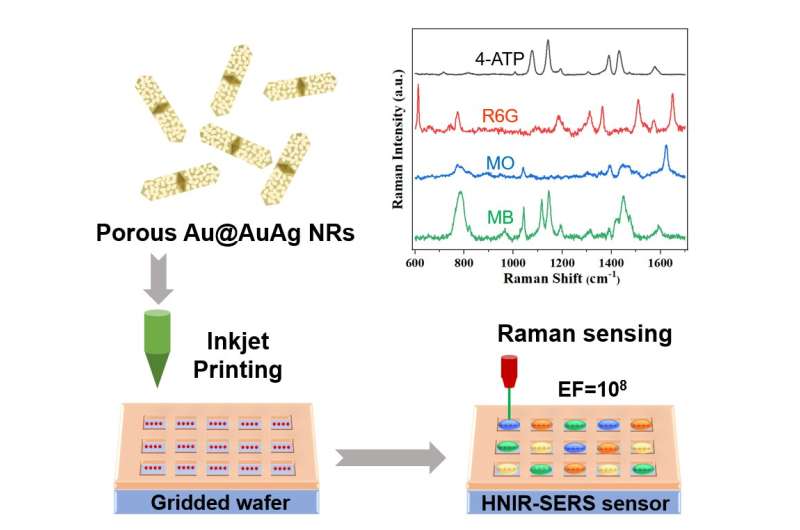
Scientists from Hefei Institute of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a high-throughput biochemical sensor based on porous Au@AuAg nanorods that can detect biochemical molecules with high specificity and sensitivity.
Their research results were published in Journal of Materials Chemistry C.
The misuse of biochemical molecules can cause significant environmental problems, so developing low-cost sensors for detecting these molecules is essential.
The sensor they've developed is called the high-throughput near-infrared surface-enhanced Raman scattering (HNIR-SERS) biochemical sensor. It's a combination of inkjet printing technology and plasma metal nanoparticles that enables high-sensitivity detection of multiple biochemical molecules in one substrate.
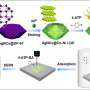
To develop this sensor, researchers utilized imprinting technology to fabricate a grid substrate with separated regions arranged in a typical cubic pattern.
They then assembled porous Au@AuAg nanorods on the substrate using inkjet printing, resulting in the formation of the HNIR-SERS sensor. This new type of sensor achieves high sensitivity and specificity in detecting multiple biochemical molecules on one substrate.
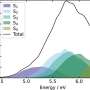
The researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of the HNIR-SERS sensor by detecting 4-aminothiophenol (4-ATP), rhodamine 6G (R6G), methyl orange (MO) and methylene blue (MB) with an enhancement factor of 108 for 4-ATP.
This development provides an effective method for realizing high-throughput and low-cost NIR-SERS sensors and could pave the way for practical applications in Raman detection chips.
More information: Yifan Wang et al, High-throughput surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensors for near-infrared detection of biochemical molecules, Journal of Materials Chemistry C (2023). DOI: 10.1039/D2TC05542B
Provided by Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences