This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Detect, bind and cut: Biomolecular action at the nanoscale
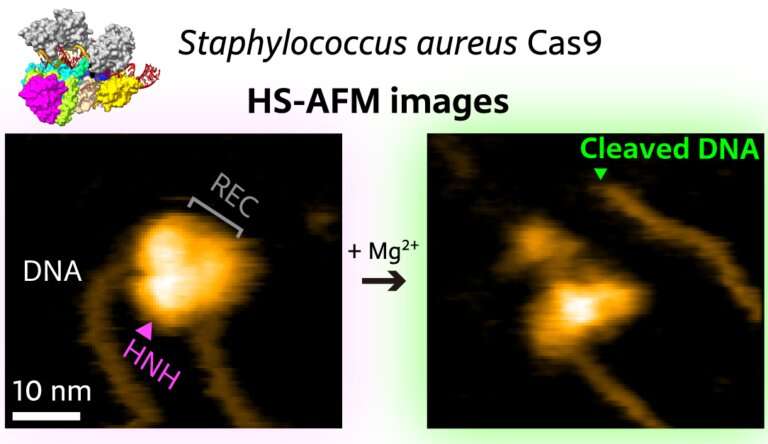
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in ACS Nano how high-speed atomic force microscopy can be used to study the biomolecular mechanisms underlying gene editing.
The DNA of prokaryotes—single-cell organisms, for example bacteria—is known to contain sequences that are derived from DNA fragments of viruses that infected the prokaryote earlier. These sequences, collectively referred to as CRISPR, for "clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats," play a major role in the antiviral defense system of bacteria, as they enable the recognition and subsequent neutralization of infecting viruses. The latter is done through the enzyme Cas9 ("CRISPR-associated protein 9"), a biomolecule that can locally unwind DNA, check for the existence of the CRISPR sequence and, when found, cut the DNA.
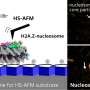
In recent years, CRISPR/Cas9 has emerged as a genome editing tool based on the notion that the Cas9 protein can be activated with artificially created CRISPR-like sequences. Sometimes, however, the wrong target is "caught" by Cas9—when the wrongly identified DNA sequence is too similar to the intended target sequence. It is therefore of crucial importance to fully understand how Cas9 binds to, "interrogates," and cuts DNA. Mikihiro Shibata from Kanazawa University and colleagues have now succeeded in video-recording the DNA binding and cleaving dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus (a particular bacterium) Cas9 by means of high-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM). Their observations will help to reach a more complete understanding of CRISPR-Cas9 mechanisms.
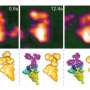
In recent years, HS-AFM has emerged as a powerful nanoimaging tool for studying molecular structures and their dynamics at high spatiotemporal resolution. For such molecular dynamics to be observable, samples need to be put on a carefully chosen substrate. For their study of Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 (SaCas9), Shibata and colleagues chemically modified a mica surface. This way, observed molecules "stick" to the substrate, but not too strongly, so that molecular mobilities are still high enough for the relevant biomolecular interactions to happen—slowed-down, within intervals of time accessible to HS-AFM.
The artificial activation of Cas9 happens via the association with a so-called single-guide RNA (sgRNA) molecule, which provides the information about the targeted DNA sequence. The scientists first observed that the SaCas9-sgRNA complex adopts a flexible modular structure that can switch from an open to a closed configuration, which enables eventual binding to the DNA. They also managed to image the cutting of DNA at the targeted site.
The researchers looked in more detail at the mechanism of detection of targeted DNA by SaCas9-sgRNA, and found evidence that it involves a selective, long-range interaction. Although the precise nature of this interaction remains unclear, Shibata and colleagues believe that hydrophobic forces between parts of the SaCas9-sgRNA complex and the DNA play a key role.
The potential importance of such long-range interactions in CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing is unexpected—up to know, the common belief has been that target DNA is identified through diffusion processes. Additional studies are needed to further explore this aspect. The scientists state, "Although the present HS-AFM observations represent direct evidence of the long-range selective interaction between SaCas9-sgRNA and its target DNA, further investigations are necessary to confirm the mechanism of search for target DNA hypothesized and illustrated in the present study."
High-speed atomic force microscopy
The general principle of atomic force microscopy (AFM) is to make a very small tip scan the surface of a sample. During this horizontal (xy) scan, the tip, which is attached to a small cantilever, follows the sample's vertical (z) profile, inducing a force on the cantilever that can be measured. The magnitude of the force at the xy position can be related to the z value; the xyz data generated during a scan then result in a height map providing structural information about the investigated sample.
In high-speed-AFM (HS-AFM), the working principle is slightly more involved: the cantilever is made to oscillate near its resonance frequency. When the tip is moved around a surface, the variations in the amplitude (or the frequency) of the cantilever's oscillation—resulting from the tip's interaction with the sample's surface—are recorded, as these provide a measure for the local "z" value. AFM does not involve lenses, so its resolution is not restricted by the so-called diffraction limit as in X-ray diffraction, for example.
HS-AFM results in a video, where the time interval between frames depends on the speed with which a single image can be generated (by xy-scanning the sample). Researchers at Kanazawa University have in recent years developed HS-AFM further, so that it can be applied to study biochemical molecules and biomolecular processes in real-time. Mikihiro Shibata and colleagues have now applied the method to study the molecular dynamics of a Cas9–DNA interaction process, which is highly relevant for on-going research on the CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing tool.
More information: Leonardo Puppulin et al, Dynamics of Target DNA Binding and Cleavage by Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 as Revealed by High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c10709
Journal information: ACS Nano
Provided by Kanazawa University